Scroll to:
Iterative Model of Elastic Deformation of a Particle Conglomerate Taking into Account the Compressibility of the Medium during Pressing
https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2218
EDN: XHHEDX
Abstract
Introduction. Briquetting and pressing of wood and other powdered materials are becoming key processes in the circular economy and recycling of wood processing waste. Accurate calculation of compaction pressure is essential for equipment selection and optimization, making the task of modeling the deformation of conglomerates both practical and economically significant. The literature addresses the mechanics of powder media, porous materials, and the modeling of elastic-plastic deformations of granular conglomerates. However, most models assume fixed mechanical characteristics or approximations that do not account for the dependence of strength and elastic properties on changing density under compression. This leaves a gap in theoretical and applied approaches to adequately calculating pressure for materials with variable density. Therefore, the objective of this work is to develop an approach for calculating the compaction pressure of a particle conglomerate as a function of the degree of elastic compression, taking into account changes in the mechanical characteristics of the medium.
Materials and Methods. In the mathematical description of the research problem, the provisions of the theory of elasticity were used. Based on the principle of superposition, the process of medium deformation was divided into a number of stages, within which the particle conglomerate received a small increment in height, and the mechanical characteristics assumed a constant value. The proposed approach for determining the compaction pressure was based on the solution to a series of inverse elastic problems in which the displacement of the upper boundary of a conglomerate of rectangular particles was specified, and the normal stress that caused this increment was sought. To account for changes in the density of the medium during deformation, the method of sequential loads was used, within each of them, the density was taken to be constant and was determined depending on the magnitude of the total compressive deformation. The Hencky strain, which has the property of additivity, was used as a measure of deformation.
Results. As part of the study, an iterative model was constructed for calculating the compaction pressure of a particle conglomerate when the mechanical characteristics change depending on the degree of elastic compression. Series of test calculations were conducted using a conglomerate of wood particles, whose Young's modulus is described by a power-law density function. At each stage of deformation, the elastic constants of the material were assumed to be constant, depending on the density of the medium. Using the equilibrium equation and the superposition principle, based on the results of solving elastic deformation problems, the compaction pressure was calculated at each loading stage, and the dependence of the compaction pressure on the magnitude of the compressive deformation and the degree of compaction was constructed.
Discussion. The obtained results of deformation of the medium taking into account the change in mechanical characteristics depending on the degree of compression showed a clearly expressed nonlinearity of the curve of dependence of the compaction pressure on the compression deformation — with an increase in pressure, both the degree of compaction of the medium and the compression deformation increase. A comparative analysis of calculations using the example of a conglomerate of wood particles under the condition of a constant density of the medium and taking into account the change in density during the deformation process revealed a significant error in estimating the compaction pressure when averaging the density or when using constant density values corresponding to the initial (undeformed) or final state.
Conclusion. The constructed iterative model allows for calculating the compaction pressure of a particle conglomerate, taking into account changes in mechanical properties under elastic compression. The proposed approach accounts for the nonlinearity of the compaction pressure dependence on the degree of compaction of the medium and can be applied to briquetting processes for wood waste.
Keywords
For citations:
Andrianov I.K., Ivanov S.N., Chepurnova E.K. Iterative Model of Elastic Deformation of a Particle Conglomerate Taking into Account the Compressibility of the Medium during Pressing. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(4):290-299. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2218. EDN: XHHEDX
Introduction. Materials with density-dependent mechanical properties are found in various industrial applications. These include granular media, wood particle aggregates, composite materials, and others. The behavior of such materials can differ significantly from the classic case, where properties remain constant and are independent of density. Some issues related to assessing the strength and stiffness of granular media are discussed in [1], and for sand molds — in [2].
Currently, briquetting processes of wood particle conglomerates are widely used in the woodworking waste [3]. Therefore, it is important to describe the behavior of particles during the compacting process. The issues of assessing the compaction pressure were discussed in [4]; mechanical and thermal analysis of the characteristics of pressed blocks with wood inclusions — in [5]; assessment of the strength of wood conglomerate — in [6]. Wood sawdust is widely used in the production of building materials, processing into fuel, and briquetting. The pressing process is affected by various factors [7]: for example, storage humidity is described in [8], and the effect of temperature is specified in [9]. In addition, wood particles are used in composite materials, in particular in the production of biocomposites [10], polymeric materials [11], and multilayer composites [12].
One of the key tasks in particle deformation modeling is the selection of pressing equipment. Paper [13] is devoted to the selection of pressing machines for producing solid biofuel through granulating, briquetting, and mechanically processing biomass. When applying the conglomerate pressing procedure, it is important to model the stress-strain state during the compression process, taking into account the compaction of the medium. A change in density entails a change in the mechanical properties of the medium, which affects the accuracy of calculating the required deforming force and the selection of equipment. The development of more accurate methods for calculating compaction pressure, taking into account the compressibility of the medium, is important for creating new, efficient technologies and improving existing ones. Some aspects of the mathematical description of an elastic-plastic problem under compression for the case of constant mechanical properties are discussed in [14].
An analysis of the current state of the art shows that not all software packages are capable of accounting for changes in density and mechanical properties under deformation. Most CAE systems perform engineering calculations with given constant values of physical and mechanical properties. Therefore, the development of effective models and methods for assessing the stress-strain state of media under pressing, taking into account compressibility and changes in characteristics, is a challenge.
The objective of this study is to develop an approach for calculating the compaction pressure required to compress a particle conglomerate to a given geometry, taking into account the effect of the compaction degree on the mechanical properties of the medium. In accordance with this objective, the following tasks are set:
- to conduct a mathematical formulation of the elastic compression problem for a particle conglomerate, taking into account the compressibility of the medium;
- to build an iterative model for calculating the stress-strain state of the medium based on solving a series of inverse problems using sequential loading;
- to perform test calculations of the stress-strain state of a particle conglomerate and plot the dependence of compaction pressure on the compressive strain of the medium;
- to estimate the error in calculating compaction pressure when ignoring changes in the density of the medium during deformation.
Research Methods. We construct a calculation method for the process of deformation of a particle conglomerate taking into account the compressibility of the medium under the following assumptions:
- since the study examines the compression of the medium, the condition of continuity is assumed, meaning the particle conglomerate uniformly fills the volume under consideration;
- the mass of the medium remains constant throughout the entire pressing process;
- the compression process of the medium is considered within the limits of elastic deformation;
- the principle of superposition is observed — independently accumulated deformations at each loading stage;
- pressing is performed in an absolutely rigid matrix using an absolutely rigid friction-free punch; the layers move uniformly along the height, eliminating shear;
- the viscosity of the medium is neglected, and the pressing temperature remains constant;
- the variable mechanical characteristics dependent on the density of the medium are Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio;
- the density of the medium is a function of the compressive strain.
The geometric model of a particle conglomerate (Fig. 1) has the shape of a parallelepiped with height h and a constant square base with area S. Due to the rectangular shape of the particle conglomerate, the model is considered in a Cartesian coordinate system, where axis 0x3 is directed along the height of the parallelepiped, and axes 0x1 and 0x2 lie in the plane of the parallelepiped base.
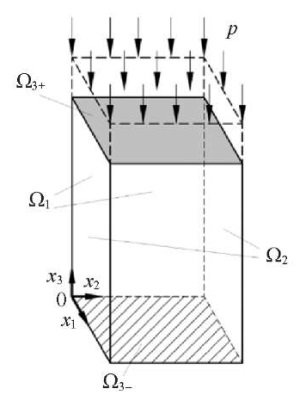
Fig. 1. Scheme of deformation of a particle conglomerate
Since the axial compressive strain increases in absolute value during compacting under pressure p, the density of the medium and, consequently, its elastic constants change. Accordingly, Young's modulus E and Poisson's ratio μ are functions of density ρ: E = E(ρ), μ = μ(ρ). We use the Hencky strain as a measure of deformation.
We divide the entire process of medium deformation into a series of loading stages, within each of which a kinematic condition in the form of a small increment of the upper boundary of the medium Δh = Δh* in height is specified. At each loading stage, we assume that the density of the medium remains constant and the mechanical properties — Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio — do not change. At subsequent loading stages, the density of the medium and the mechanical properties also remain constant within each stage, but change depending on the magnitude of the total deformation over all previous loading stages.
We consider the solution to the inverse problem, taking the pressure increment at each loading stage Δp as the unknown value. Then, the mathematical formulation of the research problem in accordance with the accepted assumptions will include the following system of equations:
- static equations:
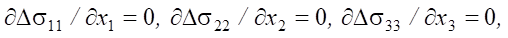 (1)
(1)
- physical equations:
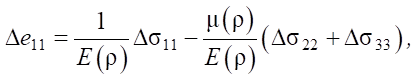 (2)
(2)
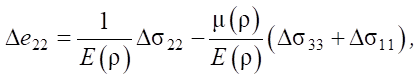 (3)
(3)
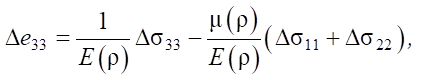 (4)
(4)
- geometric relationships:
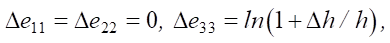 (5)
(5)
- boundary conditions:

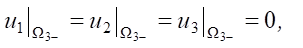

 (6)
(6)
where Δσ11, Δσ22, Δσ33 — stress increments; Δe11, Δe22, Δe33 — increment of elastic deformations; 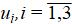 — displacement components.
— displacement components.
Based on differential equations (1) and condition (6), we arrive at the relations: Δσ11 = const; Δσ22 = const; Δσ33 = –Δp.
Considering that there are no displacements in the plane 0x1x2, according to relations (3), (5), the system of equations (2), (3) can be written as:
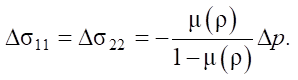 (7)
(7)
Substituting relations (5) and (7) into equation (4), we express the pressure increment in the following form:
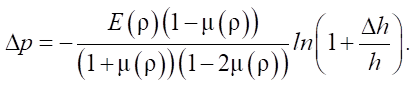
Thus, when constructing the calculation algorithm, we specify a discrete change in the height of the conglomerate depending on the loading stage:
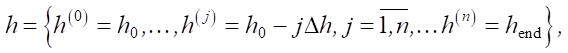
where h0 — initial height corresponding to the undeformed state of the conglomerate; hend — final height of the conglomerate after all stages of loading; j — loading stage.
Since the change in the height of the conglomerate is known, it is possible to determine the increment of deformation in height within each loading stage:

The total deformation at the current stage of loading is determined according to the superposition principle:
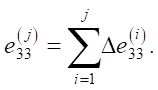
It should be noted that the selection of the Hencky strain as a measure of deformation is due to its additivity, unlike relative strain, which allows for the summation of deformations at individual loading stages. Moreover, the Hencky strain allows for calculations at large deformations.
Considering that the mass of the conglomerate and the base area remain constant: m = const, S = const, we proceed to the continuity condition in the form: ρ0h0 = ρh, from which the density of the medium is determined depending on the magnitude of the compressive strain 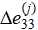 at a given loading stage according to the relationship:
at a given loading stage according to the relationship:

Knowing the density of the medium at the current stage of loading, Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio at each stage of loading are determined in accordance with the degree of compaction by a certain function:
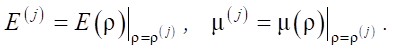
Then the increase in compaction pressure is determined as:
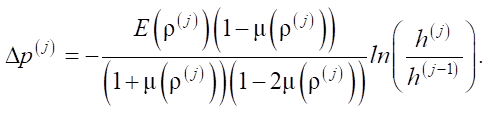
According to the principle of superposition, the components of the stress tensor at the current stage of loading are determined as:
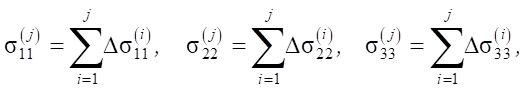
where the voltage increments at each stage are determined by the dependences:
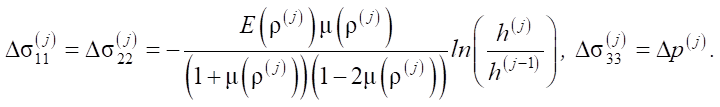
Thus, the process of compacting a particle conglomerate is represented by a series of loading stages, within each of which the medium density and elastic constants are assumed constant. At each stage, an inverse elastic problem of medium compression is solved. The input data for this problem are the density, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio, whose values are determined by the total compressive strain accumulated during the previous and current loading stages. This results in a sequence of inverse problems based on data on the change in the height of the particle conglomerate, which is used to calculate the change in compaction pressure depending on the degree of compaction of the medium.
Research Results. Based on the developed approach, a series of calculations are performed for the deformation of a particle conglomerate using sawdust as an example. Young's modulus (MPa) is described by the density function (g/cm³): E(ρ) = aρb, a = 6500, b = 3.5 [15]. The selection of a power-law dependence is due to the fact that it describes the behavior of a conglomerate of wood particles quite well, according to [15]. Poisson's ratio μ = 0.32 takes a constant value, since it is less sensitive to changes in the density of the conglomerate, as noted in [16]. Moreover, according to experimental studies [17][18], the greatest change in Poisson's ratio occurs at low values of compression, and at pressure values above 20 MPa, Poisson's ratio asymptotically approaches a constant value. The initial density of the conglomerate of wood particles in the undeformed state is taken to be: ρ0 = 0.2 g/cm³. Ten loading stages were selected for the test calculation. At each stage, the upper boundary of the conglomerate was displaced by value Δh = 10 mm, resulting in a discrete change in the height of the conglomerate: h = {200, 190, …, 110} mm. At the final loading stage, at h = 110 mm, the maximum compaction pressure was 112 MPa, and the density of the medium — 0.4 g/cm³.
Based on the results of the calculations, the dependence of compaction pressure on changes in compression strains (Fig. 2) and on changes in the density of the conglomerate of wood particles (Fig. 3) was plotted. For the comparative analysis, a series of calculations were also performed at a constant density and a constant Younge’s modulus for two extreme cases: with ρ = ρ0 = const and with ρ = ρend = ρ|h = 100 mm = const, that is, when the density of the medium corresponds to the initial undeformed state and the final deformed state at the last stage of loading; and also for the case of averaging the density of the medium: with ρ = (ρ0 + ρend) / 2 = const. The results of calculations at constant values of density and elastic constants are presented in Figure 2.
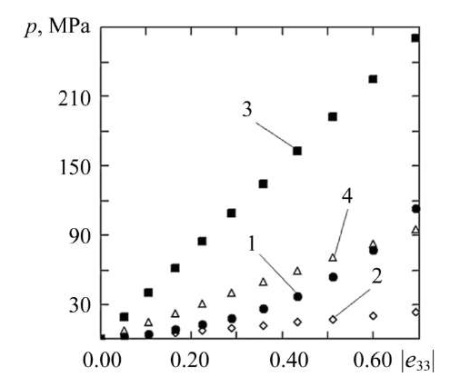
Fig. 2. Dependence of compaction pressure on compressive strain:
1 — at ρ = ρ(e); 2 — at ρ = ρ0; 3 — at ρ = ρend; 4 — at ρ = (ρ0 + ρend) / 2
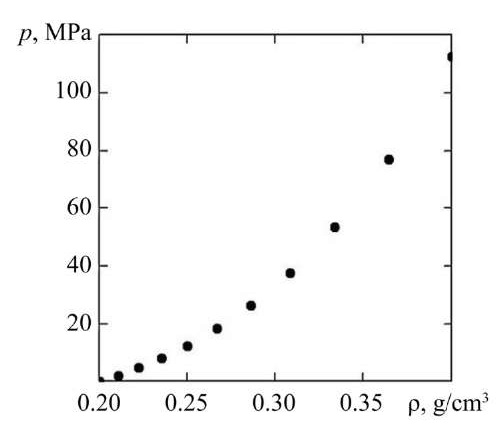
Fig. 3. Dependence of compaction pressure on the density of the medium
According to the results of solving the inverse problem of elastic compression, for the first stage of loading with a given displacement of the upper boundary of the medium h(1) = 10 mm, the increments of deformations, stresses and the required pressure were:
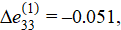
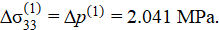
To assess the adequacy of the constructed model, a finite element calculation of the direct loading problem was performed in the ANSYS software package at a given external pressure Δp(1) = 2.041. Since the software package requires the specification of constant characteristics of the medium, the finite element calculation was performed only for the first stage of loading [19]. The calculation results of the stress-strain state under elastic compression of the medium for the first stage of loading are presented in Figure 4.
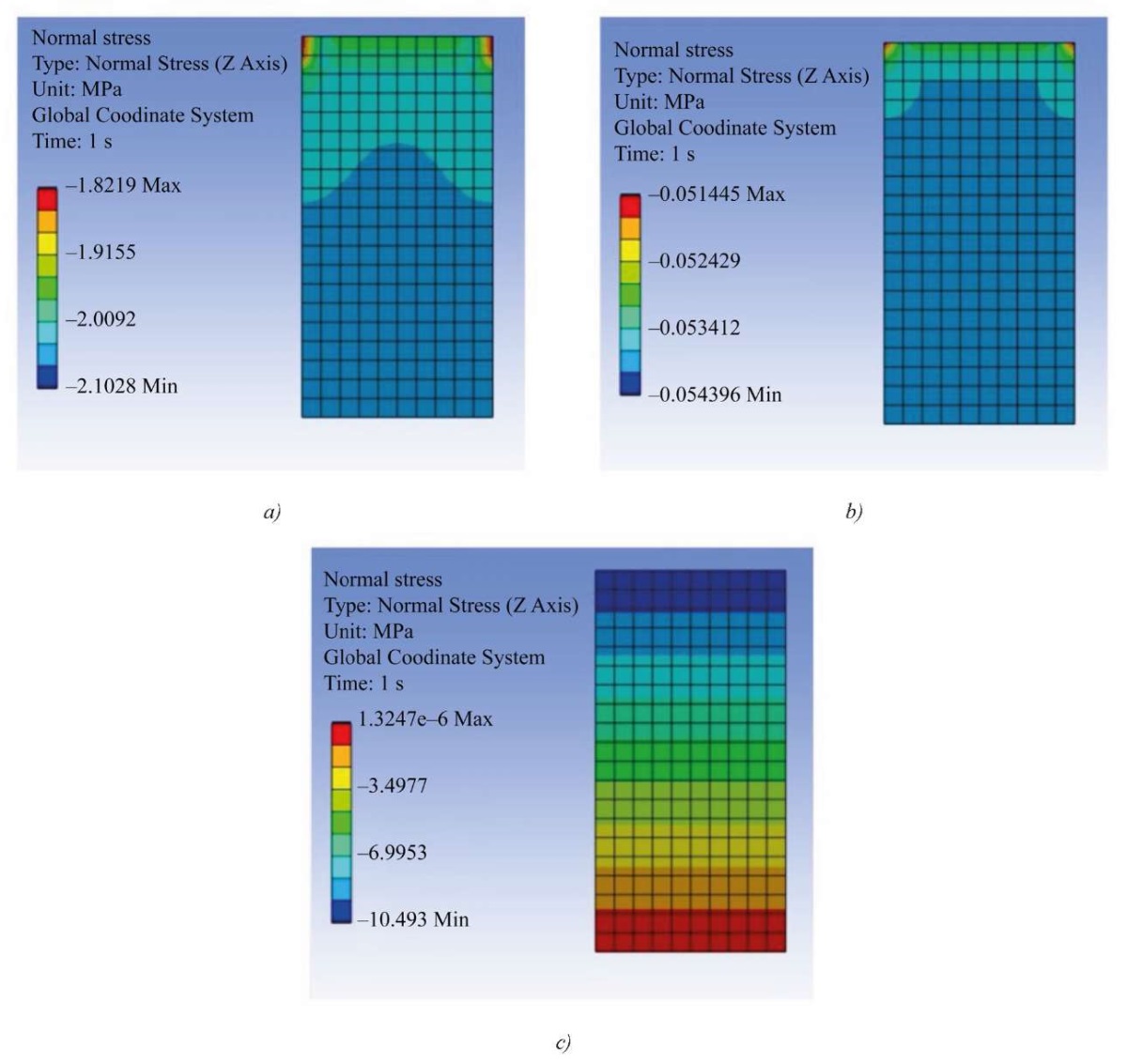
Fig. 4. Results of finite element calculation of the direct problem for the first stage of elastic compression:
a — stress distribution 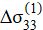 MPa;
MPa;
b — strain distribution 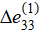 ;
;
c — displacement distribution 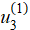 (mm)
(mm)
Discussion of Results. According to the calculation results (Fig. 2 and 3), as the magnitude of the compressive strain increases, the required compaction pressure and the degree of compaction of the particle conglomerate rise. The dependence of the compaction pressure on the degree of compaction is clearly nonlinear. The dependence of the compaction pressure on the longitudinal compressive strain (Fig. 2, curve 1) is also described by a nonlinear function, whose behavior is quite adequately approximated by a third-order polynomial function. Figure 2 shows that, at a constant density of the wood particle conglomerate, the curves for the dependence of the compaction pressure on the magnitude of the compressive strain exhibit a weakly nonlinear character. Accordingly, at a fixed density of the medium, the curves for the change in compaction pressure can be approximated by linear functions.
According to the comparative analysis, the simplification of using the density value as a constant characteristic in cases where the density of the medium changes drastically during deformation can cause significant errors. In particular, when using a constant particle conglomerate density ρ = ρ0, corresponding to the initial state, the error in calculating the compaction pressure increases to 80%, with the greatest error being attained at the maximum compaction pressure. For a constant density value ρ = ρend, corresponding to the final state of the medium, the calculation results at some loading stages differ by more than 9.4 times, and for an average density value ρ = (ρ0 + ρend) / 2 — by more than 3.4 times.
According to the data in Figure 4, the results obtained by the finite element method in solving the direct problem of the first loading stage are consistent with the results obtained in solving the inverse problem, according to the approach proposed in this study. The results presented in Figure 4 clearly demonstrate that the normal stresses and strains along the height are practically the same at each point of the body, which confirms the uniformity of their distribution along the height of the conglomerate under the action of uniform pressure at the upper boundary. It should be noted that in Figure 4 a, b there is a gradient of stresses and strains along the longitudinal axis, which is most likely a consequence of singularity (specifically in the areas highlighted in red) — one of the shortcomings of the finite element method, when there is an incorrect distribution of stresses and strains in the area of corners, with rigid fastenings, etc.
Conclusion. Based on the research results, an iterative model was developed for calculating the compaction pressure of a particle conglomerate whose mechanical characteristics depend on the degree of compaction under elastic compression. By performing iterative calculations, increasing the number of loading stages and decreasing the incremental step of the upper boundary of the conglomerate, a discrete dependence of the compaction pressure on the degree of medium compression can be constructed, which can then be approximated by a smooth curve. A series of calculations using the example of an elastic problem of pressing a wood particle conglomerate, taking into account changes in Young's modulus and the density of the medium, has revealed a nonlinear relationship between the compaction pressure and the degree of compaction of the medium and the compressive strain during compression. According to the constructed graphical dependences, the consideration of the compressibility of the particle conglomerate affects significantly the nonlinearity of the change in pressing pressure as a function of the density of the medium during deformation. The comparative analysis has shown that the calculation of the stress-strain state of media, whose density changes significantly during compaction and affects their mechanical properties, cannot be performed at constant density values due to significant errors. This allows us to conclude that the compressibility of the medium, associated with changes in the density of the particle conglomerate during compression, affects significantly the estimation of the compaction pressure. The constructed iterative model will provide a practical estimation of the maximum compaction pressure required to ensure elastic compression of the particle conglomerate to a given geometry, taking into account the dependence of mechanical properties on the density of the medium. The proposed approach can find practical application in selecting equipment for briquetting wood particles for recycling wood waste. Further research focuses on developing mathematical models for calculating the stress-strain state and compaction pressure during the deformation of particle conglomerates using complex-geometry molds.
References
1. Nazarenko VA, Pushkarev OI, Goncharova AV. Monitoring the Quality of Grinding Materials on the Basis of Their Granular Strength. Russian Engineering Research. 2009;29(10):1056–1058. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X09100219
2. Mambetaliev TS. One-Dimensional Model of the Process of Pulsed Compaction of Sand Forms. Izvestiya VUZov Kyrgyzstana. 2015;(7):20–23. (In Russ.)
3. Mikheevskaya MA, Burmistrova DD, Storodubtseva TN. Theoretical Study of Wood Waste Briquetting Taking into Account Nonlinear Strengthening of the Raw Materials. Proceedings of the St. Petersburg Forestry Academy. 2022;(240):175–185. https://doi.org/10.21266/2079-4304.2022.240.175-185
4. Chibirev OV, Kunitskaya OA, Grigoriev MF. Calculation of Needed Pressure for Sawdust Pressing during Briquetting. Repair, Reconditioning, Modernization. 2019;(2):22–25. https://doi.org/10.31044/1684-2561-2019-0-2-22-25
5. Bouzouidja R, Tingting Vogt Wu, Sbartai M. Mechanical and Thermal Analysis of Performance of Compressed Earth Blocks with Sawdust Material Stabilized with Cement. In book: Amziane S, Merta I, Page J (eds). Bio-Based Building Materials. Cham: Springer; 2023. P. 324–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-33465-8_26
6. Rudenko BD, Kulak VV. Description of the Strength of a Cement-Wood Conglomerate Made of Cavitated Wood Particles. Trends in the Development of Science and Education. 2019;57(1):30–33. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.18411/lj-12-2019-08
7. Bereziuk O, Petrov O, Vishtak I. The Impact of the Parameters of the Briquetting Process Using a Hydraulic Press on the Density Briquettes of Plant Waste. In book: Campilho RD, Ivanov V, Pinto GF, Baptista A, Silva FJG (eds). Advances in Design, Simulation and Manufacturing VIII. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Cham: Springer; 2025. P. 83–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-95218-0_8
8. Shengnan Zhao, Lujia Han, Bing Gao, Pengfei Wu and Xian Liu. Effects of Wet Storage on Compression Molding of Sawdust and Mechanism Analysis. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2019;227(2):022024. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/227/2/022024
9. Halimatuddahliana Nasution, Hamidah Harahap, Retno Riani, AI Pelawi. Effect of Pressing Temperature on the Mechanical Properties of Waste Styrofoam Filled Sawdust Composite. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2018;309(1):012034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/309/1/012034
10. Rahmani H, Algirdas A, Shestavetska A, Vaiciukyniene D. Preparation and Mechanical Characterization of Pressed Carbonized Wood Sawdust Bio-Composite. Scientific Reports. 2025;15:14981. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98658-w
11. Camilo Oliveros-Gaviria, Edwin Cumbalaza, Jose Herminsul Mina-Hernandez, Mayra Eliana Valencia-Zapata, Juan Nicolas Suarez-Bonilla, Nicolas Martinez-Mera. Wood Plastic Composite Based on Recycled High-Density Polyethylene and Wood Waste (Sawdust). Polymers. 2024;16(22):3136. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16223136
12. Adole AM, Anum I, Jamaludin MY, Suhaimi AR. Mechanical Characterization of Green Sandwich Composites from Kenaf Fiber Skins and Sawdust Core. Discover Civil Engineering. 2025;2:76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44290-025-00241-9
13. Križan P. Construction and Types of Pressing Machines. In book: Biomass Compaction. Cham: Springer; 2022. P. 5–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-89956-1_2
14. Manakhov PV, Fedoseev OB. Elastoplastic Compression of a Rectangular Body: An Alternative Approach. Russian Engineering Research. 2009;29(1):20–23. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068798X09010067
15. Vlasov YuN. Theoretical Study of the Effect of Pressing Time and Moulding Speed on Density of Sawdust Briquettes. Proceedings of the St. Petersburg Forestry Academy. 2019;(227):188–198. https://doi.org/10.21266/2079-4304.2019.227.188-198
16. Chibirev OV, Vlasov YuN, Kucher SV, Kunitskaya OA. Evaluation of Elastic Properties of Wood Particles Conglomerate. Systems. Methods. Technologies. 2017;(1(33)):140–146. https://doi.org/10.18324/2077-5415-2017-1-140-146
17. Myuller OD, V.I. Melekhov VI, Lyubov VK, Malygin VI. The Effect of Compacting Pressure on the Side Pressure Coefficient of Wood Pellets. Russian Forestry Journal. 2013;(3):97–102. URL: https://lesnoizhurnal.ru/issuesarchive/?ELEMENT_ID=56317&ysclid=mh4hl9lx33532851616 (accessed: 10.09.2025).
18. Feoktistov SI, Andrianov IK. Construction of Forming Limit Diagram for Sheet Blanks from Aviation Aluminum Alloys. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2023;23(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2023-23-1-7-16
19. Shlyakhin DA, Savinova EV. Coupled Axisymmetric Thermoelectroelasticity Problem for a Round Rigidly Fixed Plate. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2024;24(1):23–35. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2024-24-1-23-35.
About the Authors
I. K. AndrianovRussian Federation
Ivan K. Andrianov, Cand.Sci. (Eng.), Associate Professor of the Department of Aircraft Engineering and ComputerAided Design
27, Lenin Prospect, Komsomolsk-on-Amur, 681013
Scopus Author ID: 57209342766
S. N. Ivanov
Russian Federation
Sergey N. Ivanov, Dr.Sci. (Eng.), Associate Professor, Professor of the Electrical Engineering Department
27, Lenin Prospect, Komsomolsk-on-Amur, 681013
ResearcherID: Q-1869-2015
E. K. Chepurnova
Russian Federation
Elena K. Chepurnova, research laboratory assistant of the Department of Aircraft Engineering and Computer-Aided Design
27, Lenin Prospect, Komsomolsk-on-Amur, 681013
Scopus Author ID: 58188622200
This paper develops a new approach to calculating the compaction pressure of a conglomerate. The model takes into account changes in density and material properties under elastic compression. The method utilizes stepwise loading and the solution to a series of elastic deformation problems. It is shown that the dependence of pressure on compressive strain is nonlinear. It is found that accounting for density variation reduces the error in pressure estimation. The results can be applied in the design of wood waste briquetting processes.
Review
For citations:
Andrianov I.K., Ivanov S.N., Chepurnova E.K. Iterative Model of Elastic Deformation of a Particle Conglomerate Taking into Account the Compressibility of the Medium during Pressing. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(4):290-299. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2218. EDN: XHHEDX
JATS XML














































