Scroll to:
Analysis of Deformation Energy Dissipation in Reinforced-Layer Pavement
https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2184
EDN: JZUDVV
Abstract
Introduction. The design of road pavements for highways is a key stage of project development, directly impacting their durability and operational costs. In recent years, in the context of increasing traffic intensity and dynamic loads, technologies for strengthening roadbeds and bases, such as geosynthetic reinforcement and stabilized layers, have become widespread, making the study on their efficiency a challenge. Literature notes the practical advantages of reinforced layers — increased load-bearing capacity and reduced deformation. However, models for energy dissipation under dynamic impacts in structures with such layers are underdeveloped. Theoretical approaches to analyzing energy dissipation, including linear-elastic and viscoelastic models and finite element methods, have been primarily applied to traditional structures. Their adaptation to reinforced and stabilized layers requires further development, as there remain gaps in the quantitative comparison of efficiency by location and rigidity of reinforcements. The objective of the presented work is to analyze the dissipation of deformation energy in the structure of road pavements with different options for the arrangement of reinforced layers, and to determine optimal design solutions that contribute to increasing the durability of road pavements. To achieve this, it is required to formalize an energy dissipation model for structures with reinforcements, conduct a comparative analysis of different locations and rigidity levels of the layers.
Materials and Methods. The research utilized a comprehensive approach to the analysis of deformation processes in layered media using road pavements as an example, involving both a calculation tool and modern experimental equipment. As a calculation tool, a mathematical model of a layered half-space in an axisymmetric formulation in a cylindrical coordinate system was used. It was based on the solution to the system of dynamic Lame equations and allowed for the construction of amplitude-time characteristics of vertical displacements and impact loading impulse, on the basis of which it was possible to construct dynamic hysteresis loops. The FWD PRIMAX 1500 shock loading unit was used as experimental equipment, which made it possible to register similar characteristics of the road pavement response under field conditions at a load equivalent to the calculated one.
Results. The study involved numerical modeling of road pavement structures traditionally used in the Russian Federation and so-called full-depth road pavements, which were composed almost entirely of materials reinforced with binders. Dynamic hysteresis loops were constructed, and a comparative analysis of the results was provided. A numerical experiment revealed that strengthening only the subgrade layer, even without installing a reinforced base layer beneath the asphalt concrete, reduced the amount of dissipated deformation energy. It was also concluded that the elastic modulus of the underlying half-space simulating the subgrade had the greatest impact on the amount of dissipated energy.
Discussion. The greatest effect, both technical and economic, can be reached by strengthening the top of the roadbed while preserving the loose layers in the base of the road structure. This solution will bring the functioning of the road surface closer to the elastic stage and at the same time reduce the risk of cracks appearing on the surface of the pavement due to an excessively rigid layer of reinforced base.
Conclusion. On the basis of the constructed dynamic hysteresis loops, it is shown that a reduction in the magnitude of deformation energy can be obtained both by installing reinforced layers of the road surface throughout its entire depth, and by locally strengthening the underlying half-space layer and an additional base layer made of sand. The numerical experiment demonstrated that the use of reinforced base layers reduced the amount of deformation energy dissipation in the pavement structure by more than 2–3 times. Qualitative agreement between the experimental results and the numerical simulation results was shown.
For citations:
Tiraturyan A.N. Analysis of Deformation Energy Dissipation in Reinforced-Layer Pavement. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(4):324-336. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2184. EDN: JZUDVV
Introduction. One of the most important challenges facing the Russian road industry is providing a 24-year interrepair life for road pavement. One of the key approaches to solving this is improving approaches to pavement design. In the practice of the Russian Federation, it is common to design road pavement so that the rigidity of the layers increases from bottom to top, which stems from both historical design approaches and certain specific features of stress-strain state calculations using engineering methods and specialized nomograms. However, this approach does not fully reflect the efficiency of reinforced layers, such as subgrades or pavement bases.
In recent years, significant changes have occurred in the technologies and methods for calculating road pavement, associated with the introduction of software packages that implement both accurate and numerical schemes for the direct calculation of layered media [1]. In numerical methods, the most widespread are both classical finite element approaches [2], and more modern methods based on the use of spectral elements [3].
The finite element method is widely used in modeling the stress-strain state of asphalt concrete and cement concrete samples applied for the construction of road pavement and bases [4], as well as in calculating objects of limited size, typical for the practice of road and industrial-civil construction [5]. However, most of the aforementioned software packages implement a predominantly linear-elastic static formulation of the problem of determining the stress-strain state of road pavement. The wider adoption of numerical methods is constrained by the difficulty of their application to environments of unlimited volume [6]. At the same time, the actual deformation of road pavement layers is most accurately described by viscoelastic models or models that take into account the outflow of volumetric waves into infinite space [7].
As a rule, when solving problems in a viscoelastic dynamic formulation, the response of the road structure is considered either to an impact equivalent to the dynamic impact of the calculated load [8], or directly to the load from a wheel moving on the surface of the road pavement [9].
One of the most common modern solutions to this problem is the design of so-called full-depth road pavement structures, consisting entirely of layers reinforced with mineral and complex binders [10]. This approach has a number of advantages and disadvantages. The undoubted advantages include the overall high rigidity of the structures and the possibility of using recycled materials for the construction of base layers and their additional layers [11]. A number of scientific papers devoted to this topic note the good resistance of such structures to the accumulation of plastic deformations [12], the possibility of use under various natural and climatic conditions [13], and high manufacturability [14]. Disadvantages include high cost and, often with excessively increased rigidity of the base layers, a strong probability of cracking [15]. One of the most common types of crack formation for such structures is reflective cracking [16]. Some authors also note the need to take into account the specific properties of such structures in cold areas [17], and the influence of various types of defects on changes in the service life of the coating [18].
The concept of “perpetual” road pavement is well known. It involves increasing the rigidity of the structural layers of the road pavement from top to bottom, that is, when materials with a higher modulus of elasticity than asphalt concrete pavement layers are used as the base layer [19]. Such structures do provide extremely long interrepair life, which allows for the replacement of only the upper wear layers [20]. However, it is obvious that the cost and reliability of such structures are undoubtedly extremely high and often not reasonable [21]. Moreover, issues of providing proper adhesion between structural layers of different rigidity require additional research [22].
Thus, it can be argued that there are numerous approaches to pavement design, which, on the one hand, emphasizes the efficiency of such structures, but on the other, still leaves numerous questions unanswered. One of these is the study on deformation energy dissipation processes in layered media with reinforced layers, and, as a result, an assessment of the possibility of shifting deformation mechanisms to the elastic stage. The amount of energy dissipation is the most complete and physically-based characteristic reflecting the mechanisms of deformation in the structure of a multilayer medium, which can be measured and quantitatively assessed both by mathematical modeling tools and modern measuring equipment. Moreover, the use of this indicator is promising in the context of such a relevant area as the analysis of the life cycle of construction projects [23] and its implementation in information modeling technologies for monitoring the remaining useful life [24]. Thus, the objective of this work is to analyze the dissipation of deformation energy in the structure of road pavement with different options for the arrangement of reinforced layers and to evaluate optimal design solutions that contribute to increasing the durability of the road pavement.
Materials and Methods. The study utilized theoretical and experimental approaches to assess the deformation of the layered pavement environment. The research methodology is presented in Figure 1.
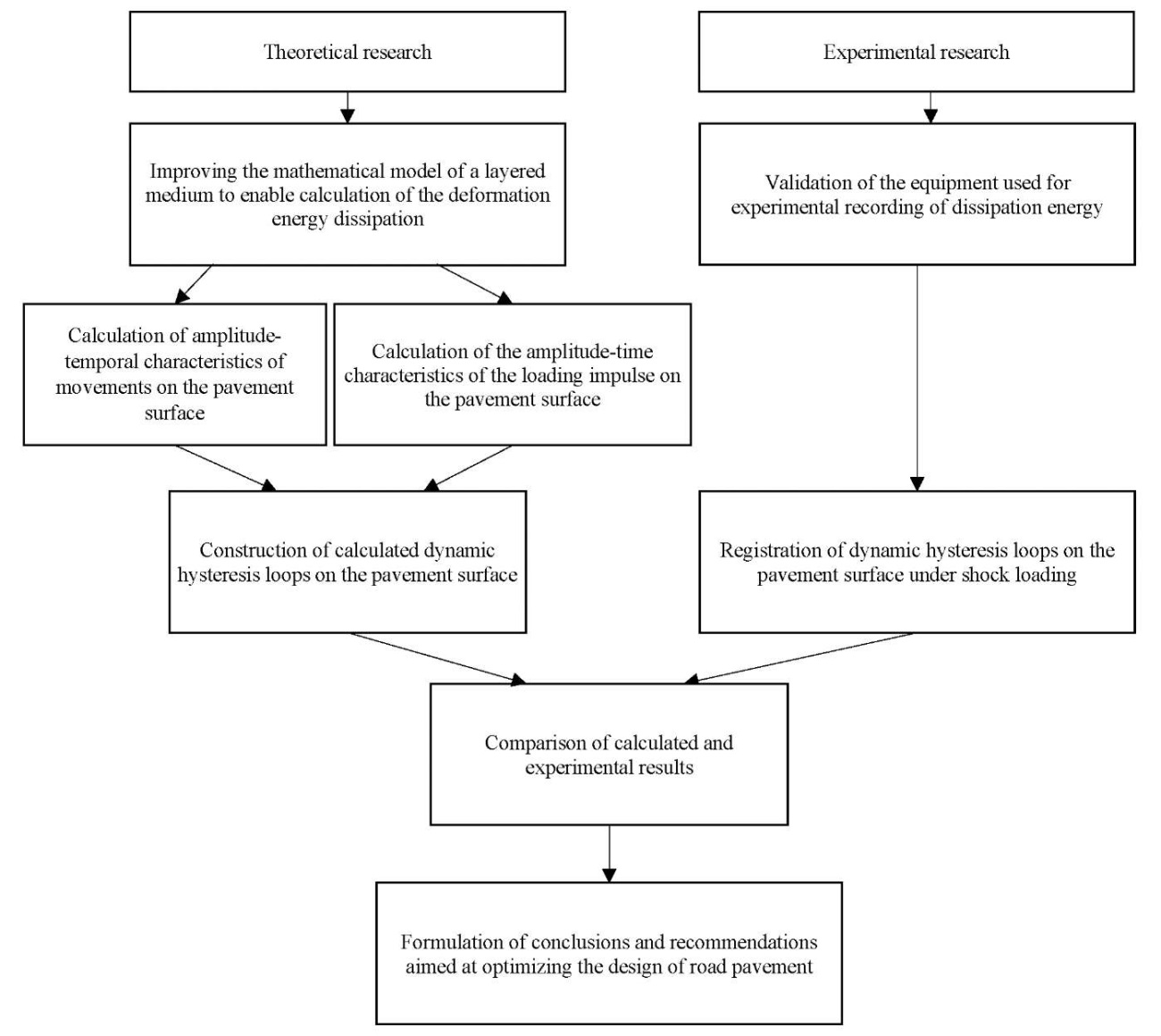
Fig. 1. Research methodology
The following road pavement designs are considered during the numerical and experimental studies. Design 1 represents a standard road pavement design in accordance with the current requirements of GOST R 71404: layer 1 is constructed of asphalt concrete, layer 2 is constructed of a crushed stone-sand mixture reinforced with a complex binder, layers 3 and 4 — dry bound macadam, and an antifrost capillary-breaking layer, respectively.
Structure 2 is an example of a full-depth road structure in which all layers are reinforced with organic or complex binders, which inevitably increases their elastic modulus. However, due to the use of expensive stabilizing and strengthening additives, as well as the inability to reduce the thickness of the structural layers within the current regulatory framework, the cost of this structure will significantly exceed that of Structure 1, which contains layers untreated with binders Structure 3 is similar in its parameters to Structure 1, but layers 2 and 5 (subgrade soil) are reinforced with a complex binder. Structure 4 involves strengthening only the subgrade soil with a binder. The structures under consideration are shown schematically in Figure 2.
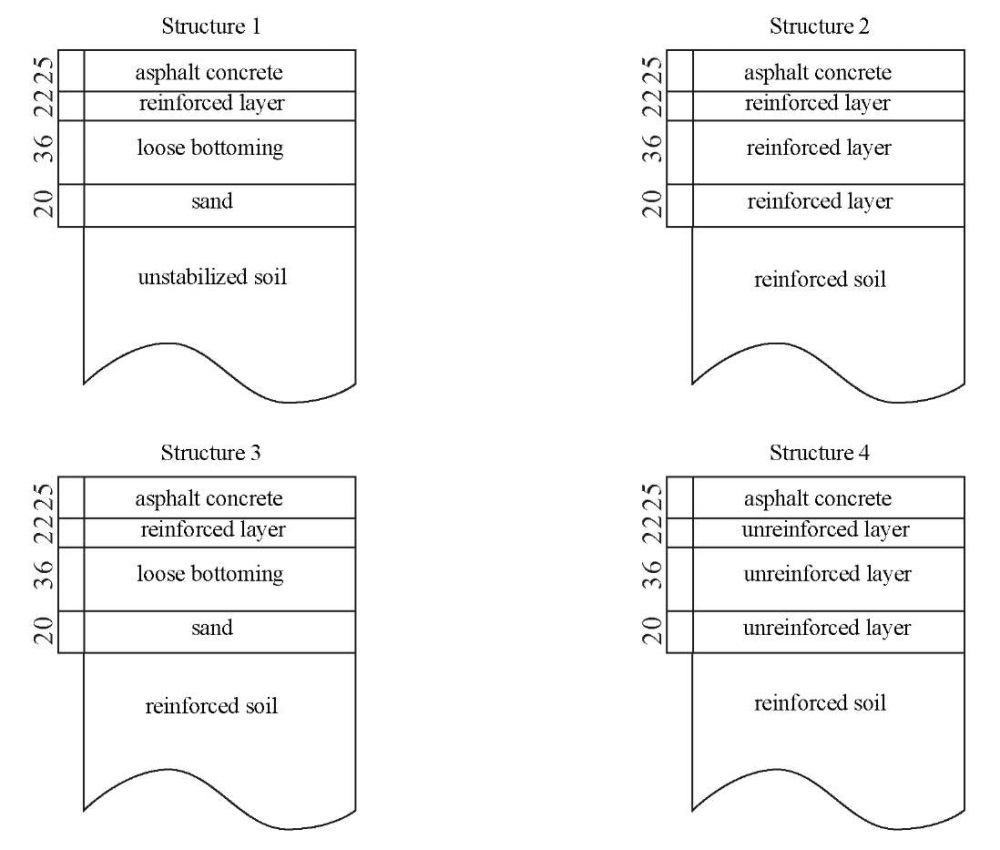
Fig. 2. Designs of simulated pavement
The theoretical approach consists in determining the stress-strain state of a layered medium under the impact of a dynamic load from a falling weight in an axisymmetric setting (Fig. 3).
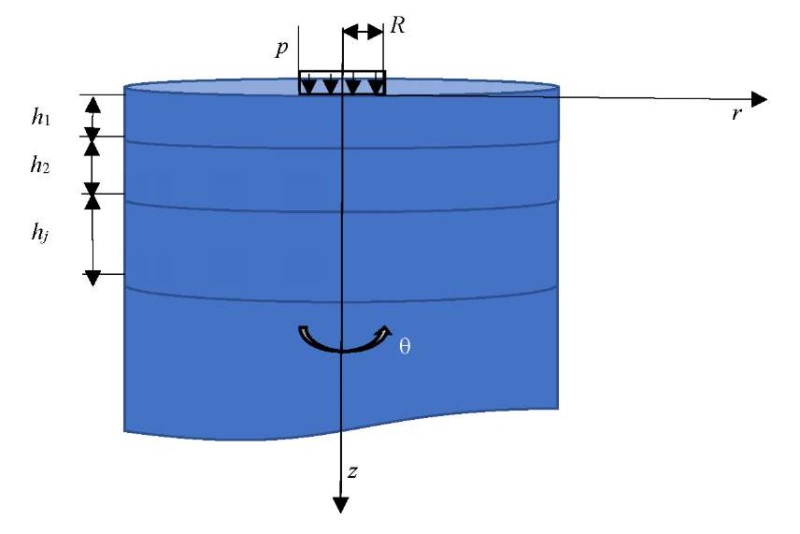
Fig. 3. Multilayer half-space
The equations of motion are as follows: [25][26]:
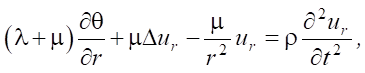 (1)
(1)
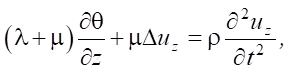
where λ, μ — Lamé coefficients; ur, uz — radial and vertical components of the displacement vector; ρ — density of the material.
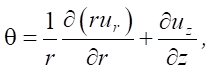 (2)
(2)
where r — radial coordinate of the point at which the displacement is found.
The Fourier transformed system of equations (1) takes the form [27]:
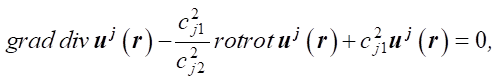 (3)
(3)
where сj1, сj2 — reduced frequencies of oscillations.
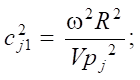 (4)
(4)
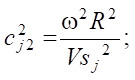
where ω — oscillation frequency, rad/s; R — radius of the loading area; Vpj, Vsj — velocities of longitudinal and transverse waves in the body.
This form of recording allows using the principle of elastic-viscoelastic correspondence, according to which the Lamé coefficients become complex, which, in turn, leads to the complex-valued nature of the reduced frequencies сj1, сj2.
Since the displacement u can be expressed through the scalar φ and vector (vortex) ψ components, the solution will be further considered in the form of the Lamé representation as:
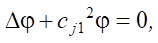 (5)
(5)
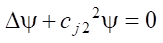
The boundary conditions of this problem in stresses are formulated as follows:
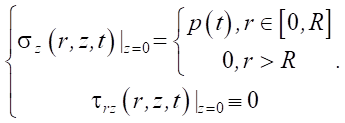 (6)
(6)
At the boundaries of the layers, conditions of rigid adhesion are set, requiring the continuity of displacements ur(r, z, t) and uz(r, z, t), and stresses σz(r, z, t), τrz(r, z, t).
At infinity, the conditions for all stress and displacement components to tend to zero are satisfied. The initial conditions of this problem are defined as follows:
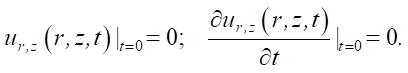 (7)
(7)
The further solution is constructed through applying the properties of the Hankel and Fourier integral transforms to the system of equations (3) and is presented in [28]. Since the solution to a non-stationary problem is considered, the method of discrete harmonic analysis is applied [29].
Experimental approach to assessing the deformation of layered road surfaces involves instrumental measurements of road pavement deformation parameters. The FWD PRIMAX 1500 shock loading unit is used for these measurements [30][31] (Fig. 4). This unit consists of a trailer with a shock loading mechanism and a measuring beam mounted on it. This beam records the vertical component of the displacement speed, which is subsequently converted into absolute values of vertical displacement. Deformation characteristics are recorded by measuring sensors. Figure 5 shows the distances from them to the dynamic loading stamp of the unit. For this study, only sensor D1, located in the center of the stamp, is used. However, in the future, other sensors could be used to evaluate deformation energy distribution processes.
The difference between FWD and other shock loading units is the possibility of practically continuous recording, with a sampling spacing of 0.002 s, of the amplitude-time characteristics of displacements on the coating surface and the amplitude-time characteristics of the shock loading pulse, based on which it is possible to construct an experimental hysteresis loop.

Fig. 4. FWD for recording vertical displacements on a layer of organomineral mixture
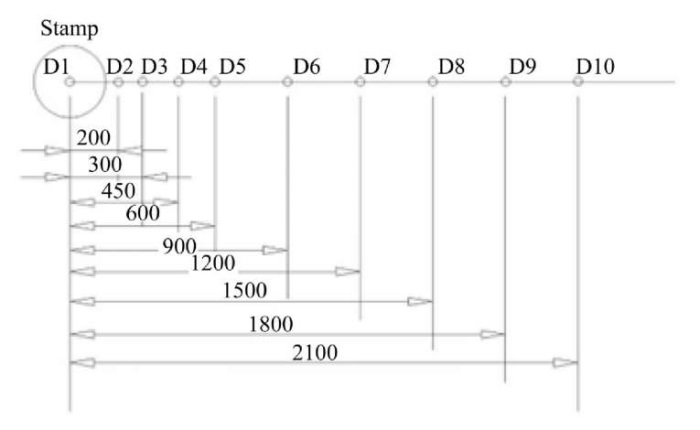
Fig. 5. Measurement design using the FWD (distances are given in mm)
This study examines road pavement structures with different rigidity ratios of the structural layers. The mechanical parameters are presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Road Pavement Designs for Modeling
|
Structure 1 |
Structure 2 |
|||||||||
|
Layers |
Е, MPa |
ν |
tgγ |
h, cm |
ρ, kg/m³ |
Е, MPa |
ν |
tgγ |
h, cm |
ρ, kg/m³ |
|
1 |
3500 |
0.30 |
0.25 |
25 |
2400 |
3500 |
0.30 |
0.25 |
25 |
2400 |
|
2 |
1000 |
0.25 |
0.15 |
22 |
2400 |
1000 |
0.25 |
0.15 |
22 |
2400 |
|
3 |
450 |
0.25 |
– |
36 |
1600 |
1000 |
0.25 |
0.15 |
36 |
2400 |
|
4 |
120 |
0.25 |
– |
20 |
1900 |
500 |
0.25 |
– |
20 |
2200 |
|
5 |
43 |
0.3 |
– |
– |
1900 |
400 |
0.3 |
– |
– |
2200 |
|
Structure 3 |
Structure 4 |
|||||||||
|
Е, MPa |
ν |
tgγ |
h, cm |
ρ, kg/m³ |
Е, MPa |
ν |
tgγ |
h, cm |
ρ, kg/m³ |
Е, MPa |
|
3500 |
0.30 |
0.25 |
25 |
2400 |
3500 |
0.30 |
0.25 |
25 |
2400 |
3500 |
|
1000 |
0.25 |
0.15 |
22 |
2400 |
450 |
0.25 |
– |
22 |
1600 |
1000 |
|
450 |
0.25 |
– |
36 |
1600 |
450 |
0.25 |
– |
36 |
1600 |
450 |
|
120 |
0.25 |
– |
20 |
1900 |
120 |
0.25 |
– |
20 |
1900 |
120 |
|
400 |
0.3 |
– |
– |
2200 |
400 |
0.3 |
– |
– |
2200 |
400 |
Research Results. The problem of determining the dynamic stress-strain state is solved and hysteresis loops are constructed on the surface of each of them using mathematical modeling for the above structures. The solution to the problem for a layered medium allows specifying the amplitude-time characteristics of the displacements u(t) on the surface of the layered medium, and the amplitude-time characteristic of the impulse F(t), from which the dynamic hysteresis loop, whose area determines the energy irreversibly dissipated in the medium, can be reconstructed [32][33]. This curve is specified parametrically in accordance with dependence (8):
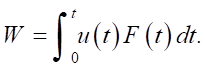 (8)
(8)
In the case of setting the dynamic hysteresis loop in the form of a data series containing information on discrete values of the actual load (Fi) and vertical displacements (ui), corresponding to a given load, the area of the hysteresis curve is determined in accordance with (9):
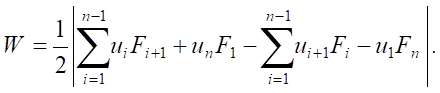 (9)
(9)
Function F(t) is described by the equation:
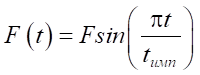 (10)
(10)
where F — design load (taken equal to 57.5 kN); t — time of observation of the object deformation (t = 0.1 s); tимп — pulse time (tимп = 0.03 s).
The possibility of constructing the amplitude-time characteristic of a sawtooth pulse and a triangular pulse, which are often used to approximate the impact loading reproduced by FWD, is also implemented.
The design load for the simulation was a 57.5 kN drop load distributed over a 30 cm diameter area, which complied with road industry regulatory requirements. The deformation energy dissipation (W) was calculated at the impact point.
Taking into account the assumption of the need for the road pavement to operate in the elastic stage, allowed in domestic regulatory documents, as well as the fact that the energy value W is essentially a function of both the mechanical and geometric parameters of the studied medium, the problem of optimal design can be reduced to the equation:
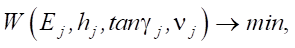 (11)
(11)
where Ej — elastic moduli of the materials of the pavement layers; hj — thickness of the pavement layers; γj — loss angles or other viscosity characteristics of the material of the layers; vj — Poisson's ratios of the materials of the layers.
The damping properties of individual layers are taken into account through introducing the loss tangent tgγ, determined on the basis of the given oscillation frequencies:
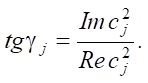
Figure 6 shows the calculated amplitude-time characteristics of the displacements on the surface of the simulated road pavements. Figure 7 presents various shock loading pulse shapes, in particular, sinusoidal, sawtooth, and triangular, corresponding to different shock load application scenarios. In this study, the sinusoidal shape is considered, as it best corresponds to the experimental loading reproduced by the FWD.
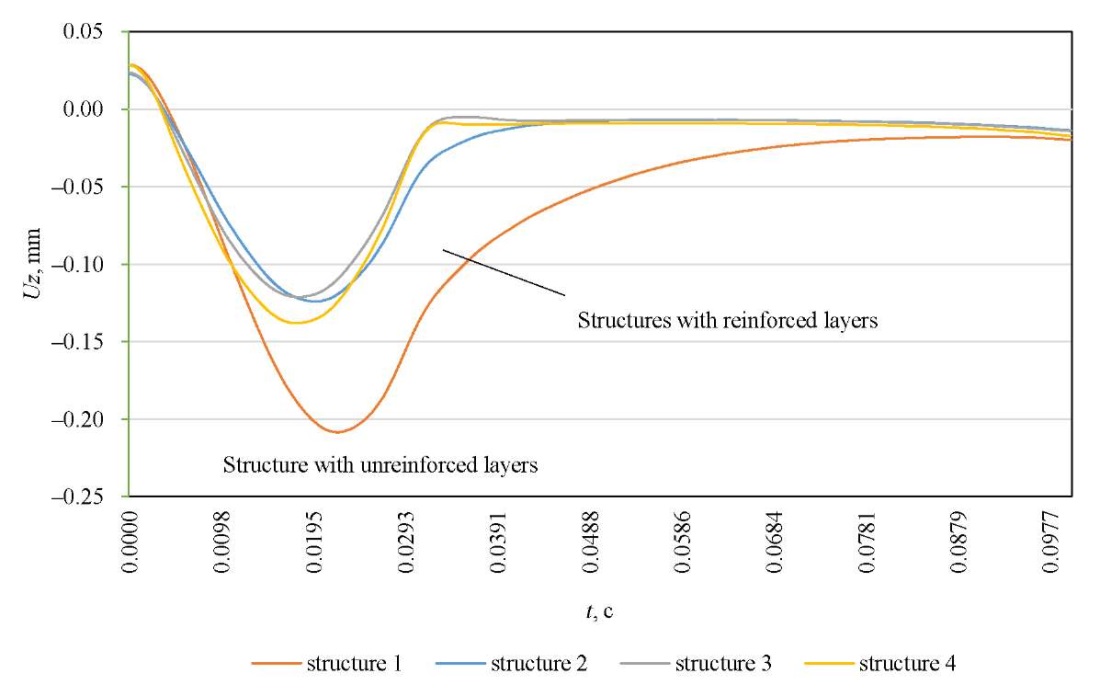
Fig. 6. Calculated amplitude-time characteristics of displacement on the surface of the studied structures
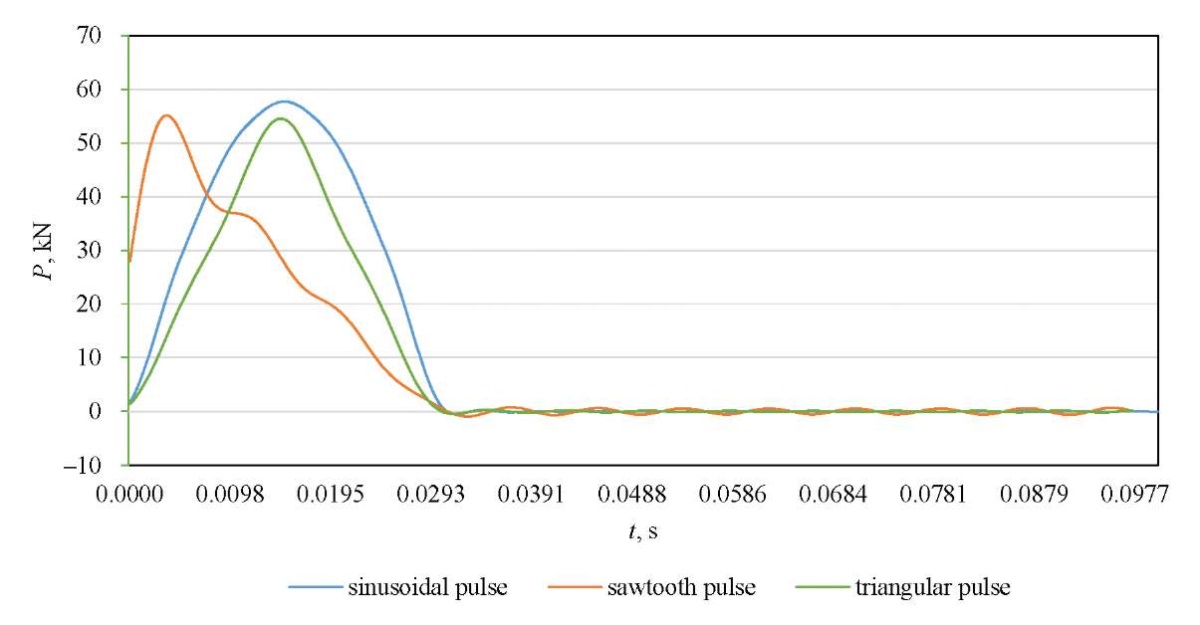
Fig. 7. Calculated load pulse shapes on the surface of the road pavement 4
The results of constructing dynamic hysteresis loops and the results of determining the dynamic deformation energy are presented in Figure 8 and in Table 2, respectively.
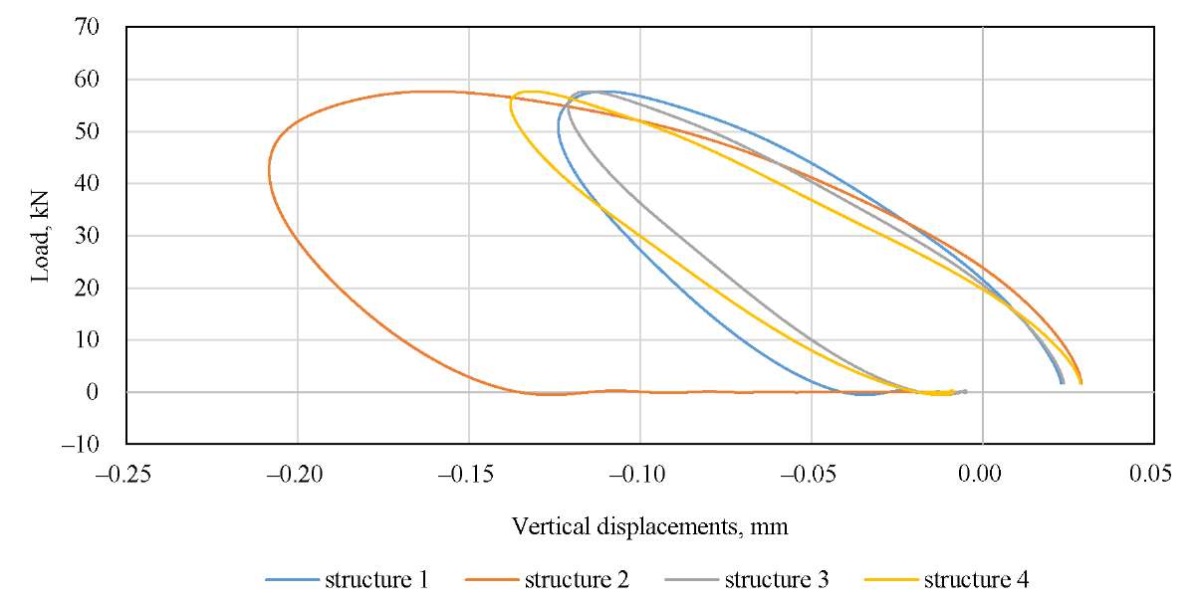
Fig. 8. Dynamic hysteresis loops calculated on the surface of road pavement structures
Table 2
Calculated Value of Deformation Energy Dissipated in Structures
|
Layers |
Deformation energy, J/m³ |
|
Structure 1 |
9.43 |
|
Structure 2 |
3.00 |
|
Structure 3 |
3.27 |
|
Structure 4 |
3.56 |
To experimentally confirm the results obtained, measurements are carried out using the FWD PRIMAX 1500 shock loading unit on the real operating road pavement, whose design is similar to structures 1, 3 and 4 shown in Table 1. The obtained experimental shapes of the dynamic hysteresis loops are shown in Figure 9, and the experimental values of the deformation energy dissipated in the structure are presented in Table 3.
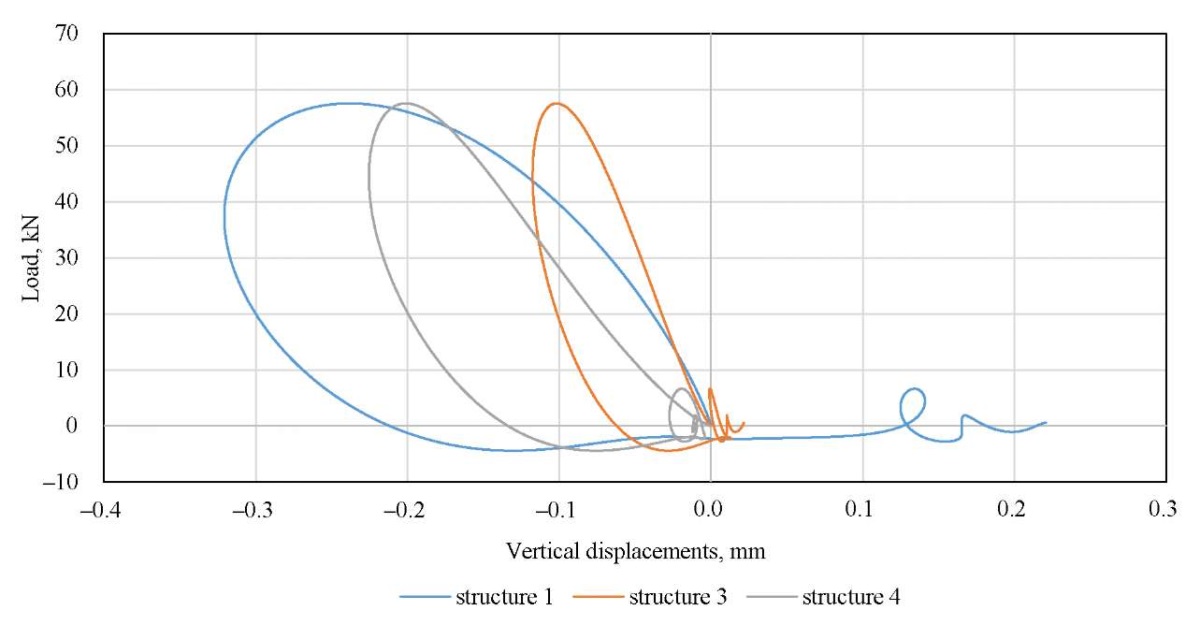
Fig. 9. Dynamic hysteresis loops recorded instrumentally on the surface of road pavement structures
Table 3
Experimental Value of Deformation Energy Dissipated in Structures
|
Layers |
Deformation energy, J/m³ |
|
Structure 1 |
9.44 |
|
Structure 3 |
3.74 |
|
Structure 4 |
4.56 |
Design options for road pavement similar to design 2 are currently undergoing feasibility studies for their applicability and have not been implemented under the field conditions of the Russian road network.
Discussion. Analyzing the data in Tables 2 and 3, we can conclude that the highest value of deformation energy dissipation is characteristic of the traditional design option 1, in which the rigidity of the structural layers increases from bottom to top. The lowest value of energy dissipation is undoubtedly characteristic of the most rigid design, 2, which assumes the construction of all layers using binder reinforcement. However, it should be noted that a nearly identical effect can be reached by the reinforcement of the working subgrade layer in the first turn. The numerical modeling has shown that strengthening only the subgrade layer, even without installing a reinforced base layer beneath the asphalt concrete, reduces the dissipated deformation energy from 9.43 to 3.56 J/m³. It can also be concluded that the elastic modulus of the underlying half-space, which simulates the roadbed, has the greatest impact on the amount of dissipated energy. Therefore, the greatest effect, both technical and economic, can be reached through strengthening the top of the roadbed while preserving the loose layers at the base of the road structure (similar to structures 3 and 4). This solution will bring the road pavement performance closer to the elastic stage while reducing the risk of cracks appearing on the road pavement surface due to an excessively rigid reinforced base layer. These modeling results were generally validated by the results of a full-scale experiment, which found that the experimental deformation energy on the surface of unreinforced structure 1, which was 9.44 J/m³, decreased to 4.56 J/m³ in the presence of a reinforced subgrade layer, and to 3.74 J/m³ in the presence of a reinforced base layer under the asphalt concrete and a reinforced subgrade layer. This fact validates the qualitative agreement between the results of in-situ and computational experiments. The research results can be applied to substantiating competing road surface design options and also be developed for use in the road maintenance industry in assessing their residual service life [34][35]. An important conclusion is the establishment of the greatest impact on the magnitude of deformation energy dissipation from the strengthening of the subgrade layer. In recent years, the issue of using various soil strengthening additives has been actively addressed at various levels [36–38]. Once more data on the strengthening of the roadbed using appropriate additives and stabilization is received, the results obtained can be applied to prove the effect of their introduction. Undoubtedly, this will require conducting research using dynamic loading and stamp testing equipment [39][40], which makes it possible to directly register dynamic hysteresis loops and load-unloading curves, and obtain the necessary information about the design characteristics of such layers. The approach presented in the study can also be efficiently developed at accelerated testing sites for road pavement [41], and used to calibrate models when their operational condition deteriorates [42].
Conclusion. Thus, as a result of the analysis performed within the framework of this research on the dissipation of deformation energy in the structure of road pavement with various options for the arrangement of reinforced layers and the assessment of the most efficient options for the arrangement of reinforced layers in the structure of the road pavement, it was established that the greatest impact on the magnitude of the dissipation of deformation energy is exerted by the strengthening of the roadbed, modeled as an elastic half-space, unlimited in thickness. This conclusion was validated by experimental studies, which revealed a similar qualitative pattern of changes in the dissipated deformation energy in a structure consisting of only unreinforced layers; a structure with a reinforced subgrade layer; and a structure with a reinforced base layer and a reinforced subgrade layer. It has been shown that the use of reinforced base layers reduces the amount of deformation energy dissipated in the road pavement structure by more than 2–3 times.
References
1. Raza MS, Sharma SK. A Review of Mechanical and Durability Properties and Microstructure of Semi-Flexible Pavement. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions. 2024;9(4):83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-024-01393-w
2. Ghanizadeh AR, Salehi M, Mamou A, Koutras EI, Jalali F, Asteris PG. Investigation of Subgrade Stabilization Life-Extending Benefits in Flexible Pavements Using a Non-Linear Mechanistic-Empirical Analysis. Infrastructures. 2024;9(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures9020033
3. Bei Zhang, Di Wang, Yanhui Zhong, Xiaolong Li, Hongjian Cai, Tao Wang. Mechanical Analysis of Semi-Rigid Base Asphalt Pavement under the Influence of Groundwater with the Spectral Element Method. Applied Sciences. 2024;14(6):2375. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062375
4. Кlyuev SV, Klyuev AV, Аyubov NА, Fediuk RS, Levkina ЕV. Finite Element Design and Analysis of Sustainable Mono-Reinforced and Hybrid-Reinforced Fibergeopolymers. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(3):171–185. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-3-171-185
5. Tretyakov DA, Osovik DS. Estimation of Stresses in a Plate with a Concentrator through Ultrasonic Measurements of Acoustic Anisotropy. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2024;24(4):307–315. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2024-24-4-307-315
6. Babushkina NE, Lyapin AA. Determination of Dynamic Stresses and Displacements under the Action of an Impact Load on a Two-Layer Structure during the Indentation Process. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2024;24(3):264–273. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2024-24-3-264-273
7. Tiraturyan AN, Lyapin AA. Analysis of the Deformation Energy Dissipation in a Layered Medium Under Dynamic Loading (On the Example of Highways). Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. 2024;61:445–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11204-024-09995-3
8. Xinnan Xu, Mohan Zhao, Yu Liu, Chaofan Wu, Yuhao Pei, Chengmiao Zhang. Falling Weight Impact Acceleration-Time Signals Analysis for Road Modulus Detection: Theoretical and Experimental Investigations. Case Studies in Construction Materials. 2024;21:e03915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03915
9. Zhenlong Gong, Yinghao Miao, Lantieri C. Review of Research on Tire–Pavement Contact Behavior. Coatings. 2024;14(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14020157
10. Yongxiang Li, Longwei Zhao, Junfeng Gao, Yanyan Ru, Haiwei Zhang. Evaluation of the Fatigue Performance of Full-Depth Reclamation with Portland Cement Material Based on the Weibull Distribution Model. Coatings. 2024;14(4):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14040437
11. Yongxiang Li, Chuangdan Luo, Kuiliang Ji, Haiwei Zhang, Bowei Sun. Laboratory Evaluation of Strength Performance of Full-Depth Reclamation with Portland Cement Material. Coatings. 2024;14(5):573. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings14050573
12. Mendoza-Sanchez JF, Alonso-Guzman EM, Martinez-Molina W, Chavez-Garcia HL, Soto-Espitia R, Delgado-Alamilla H, et al. A Critical Review of Pavement Design Methods Based on a Climate Approach. Sustainability. 2024;16(16):7211. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167211
13. Karki B, Prova S, Isied M, Souliman M. Neural Network Approach for Fatigue Crack Prediction in Asphalt Pavements Using Falling Weight Deflectometer Data. Applied Sciences. 2025;15(7):3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073799
14. Chunru Cheng, Linbing Wang, Xingye Zhou, Xudong Wang. Predicting Rutting Development Using Machine Learning Methods Based on RIOCHTrack Data. Applied Sciences. 2024;14(8):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14083177
15. Cheng Shen, Zhengguang Wu, Peng Xiao, Aihong Kang, Yangbo Wang. Experimental Research on the Anti-Reflection Crack Performance of Basalt Fiber Modified Rubber Asphalt Stress-Absorbing Layer. Materials. 2024;17(9):2013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17092013
16. Rui Ma, Yiming Li, Peifeng Cheng, Xiule Chen, Aoting Cheng. Low-Temperature Cracking and Improvement Methods for Asphalt Pavement in Cold Regions: A Review. Buildings. 2024;14(12):3802. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14123802
17. Rui Pan. Fatigue Performance Evaluation of Warm-Mixed Rubber Asphalt Mixture for Stress Absorption Layer in Cold Area. Buildings. 2024;14(12):3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14123817
18. Ashraf A, Sophian A, Bawono AA. Crack Detection, Classification, and Segmentation on Road Pavement Material Using Multi-Scale Feature Aggregation and Transformer-Based Attention Mechanisms. Construction Materials. 2024;4(4):655–675. https://doi.org/10.3390/constrmater4040036
19. Bhattacharya S, Taylor R, D’Melo D, Campbell C. Sustainable Design of Pavements: Predicting Pavement Service Life. Infrastructures. 2024;9(9):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures9090165
20. Zhen Liu, Bingyan Cui, Qifeng Yang, Xingyu Gu. Sensor-Based Structural Health Monitoring of Asphalt Pavements with Semi-Rigid Bases Combining Accelerated Pavement Testing and a Falling Weight Deflectometer Test. Sensors. 2024;24(3):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030994
21. Asres E, Ghebrab T, Ekwaro-Osire S. Framework for Design of Sustainable Flexible Pavement. Infrastructures. 2022;7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7010006
22. Chun-Hua Hsing, Jun-Han Siao, Yu-Min Wang. A Study on the Design Depth of Permeable Road Pavement through Dynamic Load Experiment. Materials. 2022;15(13):4391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15134391
23. Kryukov KM. Assessing the Benefits and Challenges of Implementing 4D Modeling in Construction. Modern Trends in Construction, Urban and Territorial Planning. 2025;4(2):75–84. https://doi.org/10.23947/2949-1835-2025-4-2-75-84
24. Al-Zgul IKh, Sheina SG, Morozova NE. Problems and Prospects of Risk-Oriented Management in Construction: A Review of Current Research. Modern Trends in Construction, Urban and Territorial Planning. 2025;4(3):65–76. https://doi.org/10.23947/2949-1835-2025-4-3-65-76
25. Tiraturyan AN. Backcalculation of Elastic Moduli for Layered Media Based on Dynamic Deformation Analysis (Example of Highways). Russian Journal of Nondestructive Testing. 2024;60(8):947–954. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061830924602010
26. Xuefeng Ye, Na Yang, Huina Chen, Manman Yang, Tingyao Wu. Damage Identification and Safety Threshold During the Construction and Operation Phases of Cast-in-Place Continuous Rigid Frame Bridges. Buildings. 2025;15(18):3282. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15183282
27. Babeshko VA, Evdokimova OV, Babeshko OM, Zaretskaia MV, Gorshkova EM, Mukhin AS, et al. On the Behavior of Materials with Defective Coating under Different Contact Conditions. Materials Physics and Mechanics. 2018;36(1):67–75. https://doi.org/10.18720/MPM.3612018_7
28. Lyapin A, Beskopylny A, Meskhi B. Structural Monitoring of Underground Structures in Multi-Layer Media by Dynamic Methods. Sensors. 2020;20(18):5241. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185241
29. Tiraturyan AN, Uglova EV, Nikolenko DA, Nikolenko MA. Model for Determining the Elastic Moduli of Road Pavement Layers. Magazine of Civil Engineering. 2021;103(3):10308. https://doi.org/10.34910/MCE.103.8
30. Zhen Liu, Bingyan Cui, Qifeng Yang, Xingyu Gu. Sensor-Based Structural Health Monitoring of Asphalt Pavements with Semi-Rigid Bases Combining Accelerated Pavement Testing and a Falling Weight Deflectometer Test. Sensors. 2024;24(3):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24030994
31. Tutka P, Nagórski R, Złotowska M. The Impact of Dynamic Effects on the Results of Non-Destructive Falling Weight Deflectometer Testing. Materials. 2024;17(17):4412. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174412
32. Xia Hua, Wael Zatar, Xiangle Cheng, Gang S Chen, Yini She, Xiaotian Xu, et al. Modeling and Characterization of Complex Dynamical Properties of Railway Ballast. Applied Sciences. 2024;14(23):11224. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142311224
33. Meng Wang, Qunding Yu, Yuanjie Xiao, Wengi Li. Resilient Modulus Behavior and Prediction Models of Unbound Permeable Aggregate Base Materials Derived from Tunneling Rock Wastes. Materials. 2022;15(17):6005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15176005
34. Fang Wang, Shiyi Zhang, Muyang Huang, Kai Liu, Chaoliang Fu. Assessment of Fatigue Life in Grouted Polyurethane Composites for Pavement Maintenance. Materials. 2025;18(8):1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081806
35. Gensheng Hu, Gongzuo Shi, Runhua Zhang, Jianfeng Chen, Haichang Wang, Junzhe Wang. Assessment of Intelligent Unmanned Maintenance Construction for Asphalt Pavement Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation and Analytical Hierarchy Process. Buildings. 2024;14(4):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14041112
36. Piechowicz K, Szymanek S, Kowalski J, Lendo-Siwicka M. Stabilization of Loose Soils as Part of Sustainable Development of Road Infrastructure. Sustainability. 2024;16(9):3592. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093592
37. Muhudin AA, Zami MS, Budaiwi IM, Abd El Fattah A. Experimental Study of Thermal Conductivity in Soil Stabilization for Sustainable Construction Applications. Sustainability. 2024;16(3):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16030946
38. Petrillo A, Fraternali F, Acampora A, Di Chiara G, Colangelo F, Farina I. Innovative Solidification and Stabilization Techniques Using Industrial By-Products for Soil Remediation. Applied Sciences. 2025;15(7):4002. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15074002
39. Jiacheng Cai, Yingchao Luo, Bing Zhang, Lei Chen, Lu Liu. Method for Extracting Impact Signals in Falling Weight Deflectometer Calibration Based on Frequency Filtering and Gradient Detection. Sensors. 2025;25(11):3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113317
40. Kuttah D. Using Repeated Light-Weight Deflectometer Test Data to Predict Flexible Pavement Responses Based on the Mechanistic–Empirical Design Method. Construction Materials. 2024;4(1):216–237. https://doi.org/10.3390/constrmater4010012
41. Ni Guangcong, Tiraturyan AN, Uglova EV, Vorobev AV. Study on Dynamic Response Characteristics of Different Asphalt Pavement Structures Based on ALF Test. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2023;23(3):241–256. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2023-23-3-241-256
42. Elshamy MM, Tiraturyan AN, Uglova EV. Evaluation of the Elastic Modulus of Pavement Layers Using Different Types of Neural Networks Models. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2021;21(4):364–375. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2021-21-4-364-375.
About the Author
A. N. TiraturyanRussian Federation
Artem N. Tiraturyan, Dr.Sci. (Eng.), Professor of the Motorways Department
1, Gagarin Sq., Rostov-on-Don, 344003
Scopus Author ID: 57190178833
This paper proposes a model for energy dissipation in a multilayer pavement. It is shown that strengthening the upper part of the roadbed reduces energy loss. The decisive impact of the subgrade rigidity on the magnitude of dissipation is established. Numerical modeling is consistent with field measurements through pulse loading. It is demonstrated that reinforced bases reduce energy dissipation by more than twofold. The results can be applied to the design of durable and cost-effective roads.
Review
For citations:
Tiraturyan A.N. Analysis of Deformation Energy Dissipation in Reinforced-Layer Pavement. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(4):324-336. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2184. EDN: JZUDVV
JATS XML














































