Scroll to:
Identification of the Activity Function of Social Network Users in a Linear Diffusion Model
https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2208
EDN: CCULZU
Abstract
Introduction. Improving the accuracy of mathematical models for disseminating information in social networks is directly related to the ability to correctly identify their parameters. In numerous papers, the fundamental complexity of this problem is actually bypassed by substituting the direct identification of the desired functions for the selection of parameters for their heuristic approximations, which inevitably leads to a decrease in both the accuracy and universality of the model. In the linear diffusion model describing the spatiotemporal dynamics of information, one of the key parameters is the function characterizing user activity. The objective of this study includes the development and numerical implementation of an algorithm for direct parametric identification of user activity functions based on a direct extreme approach, which makes it possible to completely abandon heuristic approximations, and the evaluation of its computational efficiency in comparison to the classical gradient method.
Materials and Methods. A direct extreme approach was used to solve the parametric identification problem. Unlike the classical steepest descent technique, the proposed method with adjustable descent direction adapted the search trajectory to local features of the quality functional through introducing a control parameter. The numerical solution to the direct and adjoint problems was implemented using an implicit finite-difference scheme. The method was verified using synthetic data.
Results. For the identification algorithm, an analytical expression of the gradient of the target functional was obtained through the solution to the adjoint problem. The identifiability limits of the desired parameter conditioned by the inertia of the diffusion process and the network response time were determined. A comparative study of gradient algorithms was conducted. The classical steepest descent approach demonstrated slow and uneven convergence, requiring 13,217 iterations to reach the stopping criterion, whereas the method with adjustable descent direction provided convergence to the same level of accuracy in 376 iterations.
Discussion. The obtained results confirm the theoretical assumptions about the need to take into account the spatial heterogeneity of the functional gradient when solving infinite-dimensional optimization problems. The classical gradient technique exhibits low efficiency in reconstructing nonstationary parameters due to gradient nonuniformity, while the method with adjustable descent direction reaches uniform and rapid convergence. This demonstrates that adapting the algorithm to the specifics of an infinite-dimensional problem is a key success factor. The main contribution of the research is the development of a computing apparatus for the direct determination of functional parameters, which expands the methodological arsenal for analyzing systems described by partial differential equations.
Conclusion. The key findings of this research are the development and verification of an efficient algorithm for direct identifying user activity functions in a linear diffusion model of a social network. The practical significance consists in the creation of more accurate and interpretable tools for modeling information flows without resorting to a priori approximations. The developed algorithm has demonstrated significant advantages in speed and convergence. However, the interpretation of the physical meaning of the identified function within this model requires further development. A promising direction is the application of the method to more sophisticated models that take into account the spatial heterogeneity of user activity, as well as its extension to the identification of the function vector.
Keywords
For citations:
Tolstykh M.A., Tolstykh V.K. Identification of the Activity Function of Social Network Users in a Linear Diffusion Model. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(4):363-370. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2208. EDN: CCULZU
Introduction. Social media have become an integral part of modern society, serving not only as entertainment but also as a tool for shaping public opinion and creating a community environment for various interests (everyday, political, extremist, etc.). Therefore, the tasks of studying, forecasting, and regulating the dissemination of information, as well as identifying and classifying communities on social media, are becoming hot issues. Solving these challenges requires the development of precise mathematical models of such processes.
There is a wide variety of social platforms, each with its own structure and information transfer mechanisms. The constant evolution and emergence of new algorithms for social networking operations leads to significant diversity in their mathematical models. Epidemic models SI, SIR, SEIR [1] and their modern, more sophisticated versions in the form of mean-field models [2] classify nodes (users) in a social network by state, and describe the quantitative change of nodes of a certain class. At the same time, graph models in the form of linear threshold and cascade [3] emphasize the cumulative effect of information dissemination and are often used to find opinion leaders in a social network. Each of the aforementioned models describes only specific aspects of information dissemination, without encompassing this process in its spatiotemporal fullness.
In recent years, machine learning-based models capable of accurately predicting information dissemination dynamics have gained widespread popularity [4]. However, such models typically operate on a “black box” principle and do not provide interpretable parameters (for example, virality, network throughput, or user activity). The lack of such parameters limits researchers' ability to evaluate social network clusters and manage information dissemination processes, which jeopardizes the application of models in problems requiring an understanding of the internal mechanisms of diffusion.
In [5][6], the feasibility of constructing a fundamentally general model that is not linked with the constantly changing algorithms of social network functioning is noted. In [7], in order to reach this objective, the use of the mathematical apparatus of partial differential equations, namely, the linear diffusion model, is proposed:
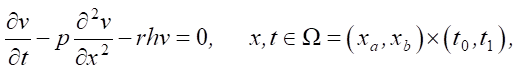 (1)
(1)
where t — time; x — distance in a network graph, measured by the minimum number of edges along which information can be transmitted V(x, t) ∈ L2(Ω) (for example, in the form of the number of reposts of a certain news item); L2 — Euclidean space of square-integrable functions.
The authors define the parameters of the model as follows: p — popularity of information (virality, speed of diffusion of information in the network); h — capacity of the social network (the maximum number of users who can take part in the dissemination of information); r — user activity (rate of growth of information in the network).
Model (1) takes into account the spatiotemporal patterns of information dissemination, and its parameters can be adjusted to reflect the characteristics of specific social networks [7]. In this case, the key problem is the task of parametric identification of the model. In general, all specified parameters should be functions: p(x), h(x), r(t). The authors of model (1) propose approximating these functions with various heuristic dependences, which leads to the problem of parametric identification of the set of coefficients-numbers included in these dependences [8][9]. This simplification does not allow us to reach maximum accuracy, which is possible only when identifying the functions directly specified, rather than their approximations, since the set of parameters included in the model may differ significantly for different social networks and even clusters of a single social network. The authors [10] reasonably point out that it is often impossible to analytically find optimal parameter functions, and classical numerical methods prove ineffective.
In [11], the problem of direct identification of function h(x) is considered. To find its optimal value, a direct extreme approach [12] is used, based on the direct minimization of the quality criterion of identification J(h) by extreme algorithms with gradient ∇J(h; x). Although an attempt was made in [11] to directly identify h(x), the problem of identifying the time function r(t) for similar models has not been systematically studied in the literature. The objective of this paper is to fill this gap through developing and numerically implementing an algorithm for direct parametric identification of the user activity function in the linear diffusion model (1) based on the direct extreme approach. The main task is to evaluate the efficiency of gradient algorithms for reaching this goal. The solution to this problem will create a methodological basis for the subsequent identification of other parameters (for example, p(x) or the simultaneous identification of a vector of parameter functions) and the transition to more complex nonlinear models. Parameters h(x) and p(x) are considered known in this paper and are taken from [5] for isolation and detailed analysis of the target problem.
Materials and Methods. To model the processes of information dissemination according to equation (1) in the studied cluster of the network graph, boundary conditions of the first and second kind are specified:
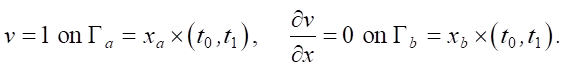
Here, we assume that the information source is located at node xa and at time t = t0 generates information v(xa, t0) in the form of a single news item. Value xb determines the distance at which the information flow disappears.
The initial condition corresponds to the absence of the news item in question in the network:
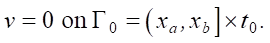
The quality criterion of model identification is specified as the deviation of the model state v from the experimentally observed ve in the real network over the entire spatiotemporal region Ω in the form of the following functional:
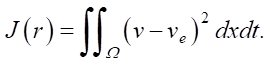 (2)
(2)
The problem of parametric identification of the optimal value of the function r⁎(t) is formulated as an extremum problem:
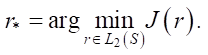
To solve this problem, an infinite-dimensional gradient algorithm is used:
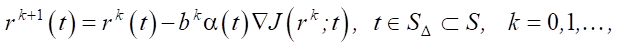 (3)
(3)
where k — iteration number; bk — step multiplier (selected using the golden section method); α(t) — parameter for regulating the direction of descent. If α(t) = 1, then algorithm (3) is reduced to the classical steepest descent method (SDM). Otherwise, this algorithm is a method with adjustable direction of descent (ADDM) [12]. Parameter α(t) regulates the direction of descent to the optimum to provide uniform convergence of the functions rk⁺¹(t) to r⁎(t) on SΔ ⸦ S, where uniform convergence is, in principle, possible. For ADDM, according to [12], the parameter for regulating the direction of descent can be set:
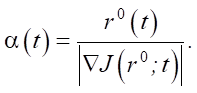
To implement algorithm (3), it is required to find an analytical expression for the gradient of the objective functional (2), which depends implicitly on the control. This is the main difficulty in infinite-dimensional identification. The gradient is found through solving the adjoint problem, the technique for obtaining which is widely described in the literature [13][14].
To evaluate the efficiency of the solution to the problem of parametric identification of the user activity function in model (1) through the direct extreme approach (3), the following test problem was set.
The original and adjoint linear parabolic equations were solved numerically using the implicit Crank-Niсolson finite-difference scheme by the sweep method. The spatiotemporal grid was defined by the values n = 50, m = 500. This corresponded to the distance of five edges of the network graph over which the news spread from the source, and time t1 – t0 = 72 hours. It was assumed that tΔ = 5 hours.
To construct the synthetic data ve, parameters p and h were assumed to be known and were taken from [5]:
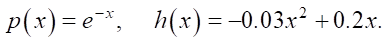
A test optimal value was set, which was also proposed in [5]:
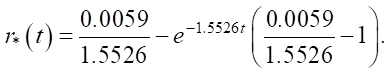
The direct problem for model (1) was solved. The resulting state v(x, t) was taken as the “experimental” ve(x, t). Next, the initial approximation r⁰(t) = 0.3was specified, and the iterative process of solving the inverse identification problem using the extremal algorithm (3) began to recover function .
The condition for stopping iterations was the following criterion for the practical termination of convergence:
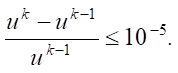
Research Results. For algorithm (3), the gradient is found:
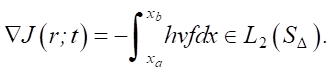 (4)
(4)
It is determined through solving the following adjoint problem f:
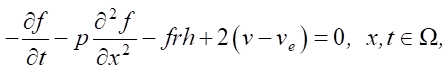 (5)
(5)
with the corresponding boundary and initial (terminal) conditions:
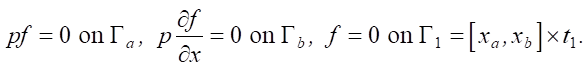
The adjoint problem is solved in the reverse time direction from the initial zero state f on Г1. For a nonoptimal value r(t), after some time tΔ due to free term 2(v – ve) in equation (5), a nonzero state f is formed. If we conduct a controllability analysis, we obtain a controllability set on which function r(t) can be identified:
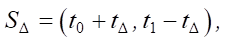 (6)
(6)
where tΔ, on the one hand, is the waiting time for network users to begin reacting to the published news. Identifying user activity before their reaction is impossible. On the other hand, this is the onset time of the impact of term 2(v – ve) in the adjoint problem on the entire spatial domain of the network cluster under consideration.
Figure 1 shows the initial value of the gradient. The identification results are presented in Figure 2 a. The convergence of the method ends at iteration k = 13,217 with nonuniform convergence on SΔ. The dash-dotted curve is an example of the value of function r²⁰(t) at the 20th iteration.
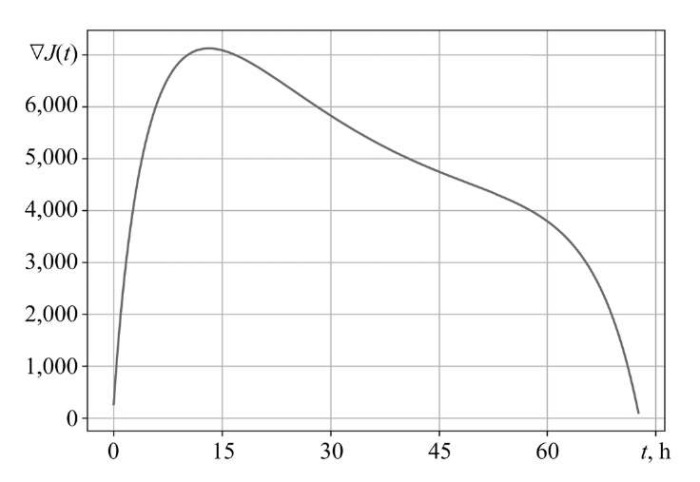
Fig. 1. Initial value of gradient ∇J (r⁰; t)
The results of the ADDM identification are shown by the dotted curve in Figure 2 b. Convergence was completed after k = 376 iterations. The resulting function r³⁷⁶(t) visually matches the exact test value r⁎(t). The dash-dotted line is an example of r(t) at iteration k = 20. The final value of the objective functional in both methods was approximately the same.
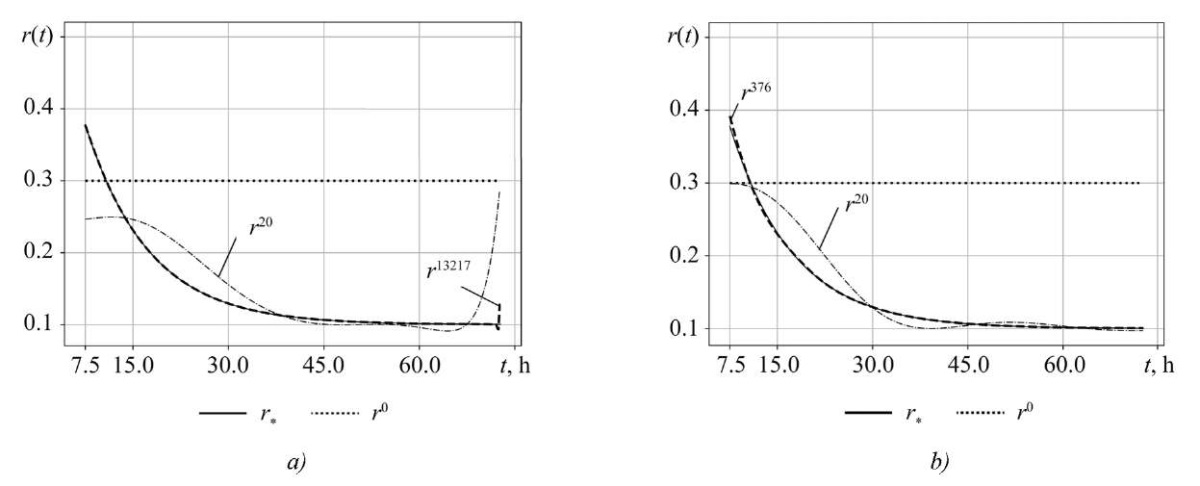
Fig. 2. Identification of r(t): a — by SDM; b — by ADDM
Discussion. The obtained results allow us to draw a number of important conclusions about the nature of the identification problem and the efficiency of the proposed method. The significant nonuniformity of the initial gradient ∇J(r⁰; t) (Fig. 1) with a uniform initial approximation r⁰(t) is a direct consequence of the spatiotemporal dynamics of model (1) and limited controllability (6) of the system at the edges of the interval S. This explains why the classical SDM, which does not take this heterogeneity into account, exhibits slow and uneven convergence (Fig. 2 a). The algorithm spends significant computational resources on compensating for the gradient features, which leads to the need for 13,217 iterations.
In turn, the ADDM effectively compensates for this heterogeneity due to parameter α(t), adapting the search direction to the local features of the functional. This is confirmed by the uniform rk(t) → r⁎(t) on the entire set SΔ (Fig. 2 b) and a reduction in the number of iterations by two orders of magnitude (376 versus 13,217). This result is in good agreement with the theoretical assumptions presented in [12] and confirms that for infinite-dimensional problems, the key factor is not simply minimization, but taking into account the heterogeneity of the gradient functional.
As for consistency with previous research, success in direct identification r(t) develops the ideas embedded in [11] for identifying h(x), and demonstrates the universality of the direct extreme approach for functional parameters in distributed systems. At the same time, our approach offers a solution to the problem identified in [10], where the inefficiency of classical numerical methods was noted.
For comparison, similar problems for systems of ordinary differential equations in the identification of a vector of numbers were considered in [15]. It was shown that the problem was not in the problem itself, but in the need to use specialized adaptive algorithms. Establishing the domain of identifiability SΔ is also an important methodological contribution.
This result highlights a fundamental limitation associated with the inertia of the diffusion process and the time it takes for the network to react, which must be consicdered when correctly formulating such inverse problems.
Conclusion. This paper addresses the pressing problem of direct parametric identification of the user activity function r(t) in a linear diffusion model (1) describing the dissemination of information in a social network. The developed and verified algorithm, based on a direct extreme approach with an adjustable descent direction, has demonstrated a more than twofold improvement in convergence rate compared to the classical gradient method, proving its high efficiency for this class of problems.
The practical significance of this research lies in the creation of a computational tool that eliminates a priori heuristic approximations of parameters and moves to direct function reconstruction, critically increasing the accuracy and validity of information dissemination models. This opens up opportunities for developing more reliable systems for predicting and managing information flows in social networks.
The basic limitation of the current work is the use of synthetic data for method validation. Also, the interpretation of the physical meaning and dimensionality of r(t) function itself requires further in-depth study. Future research will focus on the development of model representations and adaptation of the proven method to more complex nonlinear models. A key challenge for the future is to expand the method for simultaneous identification of several functional parameters, which is a more complex but also more practically valuable task.
References
1. Mei Li, Xiang Wang, Kai Gao, Shanshan Zhang. A Survey on Information Diffusion in Online Social Networks: Models and Methods. Information. 2017;8(4):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8040118
2. Glukhov AI, Shishlenin MA, Trusov NV. Modeling the Dynamics of Social Protests: Mean Field Games and Inverse Problems. Differential Equations. 2025;61(6):802–822. https://doi.org/10.7868/S3034503025060067
3. Alshahrani M, Zhu Fuxi, Sameh A, Mekouar S, Sheng Huang. Efficient Algorithms Based on Centrality Measures for Identification of Top-K Influential Users in Social Networks. Information Sciences. 2020;527:88–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.060
4. Dritsas E, Trigka M. Machine Learning in Information and Communications Technology: A Survey. Information. 2025;16(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16010008
5. Haiyan Wang, Feng Wang, Kuai Xu. Modeling Information Diffusion in Online Social Networks with Partial Differential Equations. Cham: Springer; 2020. 144 p. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1310.0505
6. Ying Hu, Rachel Jeungeun Song, Min Chen. Modeling for Information Diffusion in Online Social Networks via Hydrodynamics. IEEE Access. 2017;5:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2605009
7. Feng Wang, Haiyan Wang, Kuai Xu, Jianhong Wu, Xiaohua Jia. Characterizing Information Diffusion in Online Social Networks with Linear Diffusive Model. In: Proc. IEEE 33rd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems. New York City: IEEE; 2013. P. 307–316. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDCS.2013.14
8. Zvonareva TA, Kabanikhin SI, Krivorotko OI. Numerical Algorithm for Source Determination in a Diffusion–Logistic Model from Integral Data Based on Tensor Optimization. Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics. 2023;63(9):1513–1523. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0044466923090193
9. Krivorotko O, Kabanikhin S, Shuhua Zhang, Kashtanova V. Global and Local Optimization in Identification of Parabolic Systems. Journal of Inverse and Ill-Posed Problems. 2020;28(6):899–913. https://doi.org/10.1515/jiip-2020-0083
10. Zoppoli R, Sanguineti M, Gnecco G, Parisini Th. The Basic Infinite-Dimensional or Functional Optimization Problem. In book: Neural Approximations for Optimal Control and Decision. Cham: Springer; 2020. P. 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29693-3_1
11. Tolstykh VK. Direct Extreme Approach for Optimizing Distributed Parameter Systems. Donetsk: Yugo-Vostok; 1997. 177 p. (In Russ.)
12. Tolstykh MA. Identifying the Capacity of a Social Network. Moscow University Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics. 2024;48:59–64. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0278641924010084
13. Miele A. Theory of Optimum Aerodynamic Shapes. New York: Academic Press; 1965. 455 p.
14. Marchuk GI, Shutyaev VP. Adjoint Equations and Iterative Algorithms in Problems of Variational Data Assimilation. Proceedings of the Steklov Institute of Mathematics (Supplement Issues). 2012;276(2):138–152. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0081543812020113
15. Kabanikhin SI, Krivorotko OI. Optimization Methods for Solving Inverse Problems of Immunology and Epidemiology. Journal of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics. 2020;60(4):590–600. https://doi.org/10.31857/S0044466920040109.
About the Authors
M. A. TolstykhRussian Federation
Margarita A. Tolstykh, Junior Research Associate, Mathematics Center
24, Universitetskaya Str., Donetsk, 283001, Donetsk People's Republic
V. K. Tolstykh
Russian Federation
Viсtor K. Tolstykh, Dr.Sci. (Phys.-Math.), Dr.Sci. (Eng.), Professor of the Computer Technology Department
24, Universitetskaya Str., Donetsk, 283001, Donetsk People's Republic
Scopus Author ID: 6701477776
This paper proposes an algorithm for direct identification of the activity function. The algorithm is based on an extremal approach with a controlled descent direction. An analytical expression for the gradient is obtained through the solution to the adjoint problem. It is shown that the convergence of the proposed method is accelerated tenfold compared to the gradient method. The limits of identifiability are related to the inertia and response time of the network. The method is applicable to modeling information flows in social networks.
Review
For citations:
Tolstykh M.A., Tolstykh V.K. Identification of the Activity Function of Social Network Users in a Linear Diffusion Model. Advanced Engineering Research (Rostov-on-Don). 2025;25(4):363-370. https://doi.org/10.23947/2687-1653-2025-25-4-2208. EDN: CCULZU
JATS XML














































