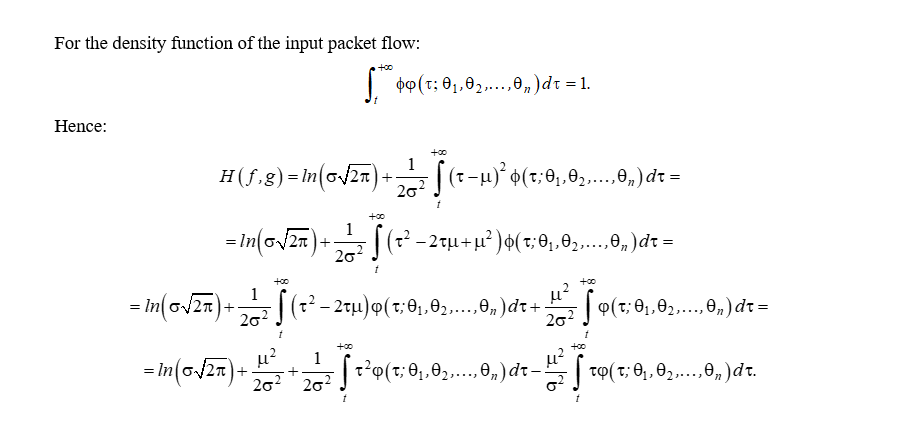MECHANICS
Introduction. Acoustic anisotropy is measured during ultrasonic nondestructive testing. It estimates the magnitude of stresses by the acoustoelasticity method. The literature describes in detail the application of this approach in the case of a biaxial strength of extended structures: main pipelines, rail strings, steam generators, and others. They assume the presence of a uniform field with zero or weak gradients of stresses and deformations. However, the problem of timely detection and assessment of critical stresses caused by local concentrators through ultrasonic testing has not been solved. The presented material is intended to fill this gap. The work is aimed at determining the possibilities of the acoustoelasticity method to estimate the difference in the main biaxial stresses around the concentrator — a circular cutout in a rectangular plate.
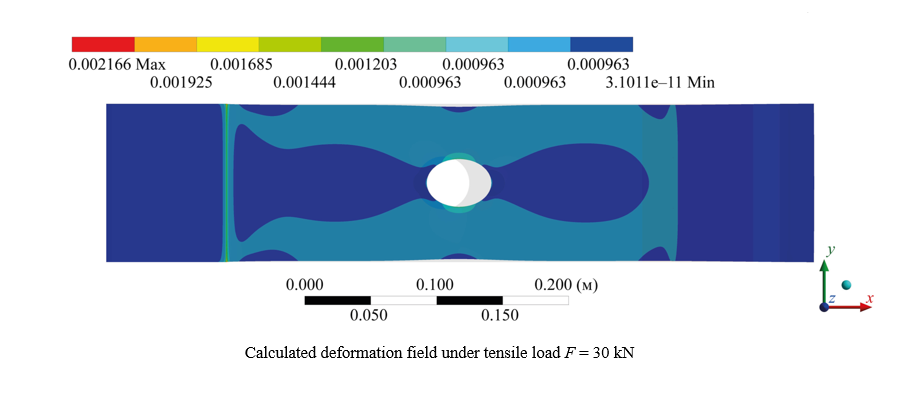
Materials and Methods. A 510×120×15 mm plate with a central hole of 40 mm in diameter was cut from a sheet of commercial-purity aluminum of the AMc brand (AW-3003 according to ISO) across the rolling direction, and subjected to uniaxial step loading in an Instron-8850 testing machine. For ultrasonic measurements, an acoustic sensor with a carrier frequency of 5 MHz was used. The stresses were calculated by solving the problem of stretching an isotropic linear-elastic plate in the ANSYS finite element modeling package and by the relations of the plane Kirsch problem obtained in the polar coordinate system.
Results. The research allows us to state that the results of analytical and numerical calculations largely coincide only for points located near the zone of greatest stress concentration. In all other cases, the indicators differ several times in sign and modulus. The difference is explained by the fact that Kirsch's approach assumes the action of compressive stresses in the area of location of some points, but this factor is absent if we are talking about a real plate. It has been established that in the area of material with predominant tensile stresses, the acoustoelasticity method allows for a quantitative estimate of their difference with an error not exceeding the engineering one. Calculations based on the Kirsch relations correlate with the others only at points with the maximum concentration of tensile stresses.
Discussion and Conclusion. The results of the study provide applying the acoustoelasticity method to estimate the magnitude of tensile biaxial stresses in the area around the fabrication holes. They are consistent with well-known scientific results and make it possible to rationally select the measurement points of acoustic anisotropy. The results of this scientific work can be applied in ultrasonic non-destructive testing using the acoustoelasticity method.
Introduction. When applying hydraulic fracturing technology to increase the efficiency of formation fluids, high-pressure pumps with a crosshead drive assembly are used. The major problem in the operation of these pumps is the wear of the crosshead guides. The crosshead is a flat sliding friction pair, leading to wear of the plunger seals and a decrease in the basic pump performance indicators. To solve this problem, it was previously proposed to use new materials and antifriction coatings, original designs of friction units, etc. However, a detailed description and solution to the problem under consideration has not been found in the literature at present. The objective of this study is to determine, under maximum load, the influence of the unit design, process temperature and pressure in the lubrication system on the values of the parameters that provide for the hydrostatic mode for a flat thrust bearing in a crosshead-guide unit of a high-pressure plunger pump.
Materials and Methods. The parameters were determined by the simulation technique using modal analysis applicable in the case of high dynamic loads acting on the studied unit. The calculation of the hydrodynamic parameters of the lubricating layer was based on the combination of the Reynolds model and the Stokes model in numerical modeling. The study was conducted using a calculation model representing a section of a plunger pump, considered as “flexible bodies” model, in the field of gravity forces. The mathematical dependences of the parameters under consideration were presented in the form of regression equations obtained from the results of a numerical experiment.
Results. The maximum load on the lower crosshead guide was determined, for which further hydrodynamic studies were conducted. Factors influencing the process were studied — gaps filled with lubricant (depending on the design of the unit), temperature, and pressure in the lubrication system. Mathematical dependences of the influence of the considered factors on the values of the parameters determining the establishment of the hydrostatic mode were obtained.
Discussion and Conclusion. The obtained mathematical models show the degree and influence of the factors under consideration on the studied parameters of the hydrostatic lubrication mode of the unit — the force acting on the crosshead from the lubricating layer, and the mass flow rate of the lubricant at the outlet of the system. It is found that the greatest influence is exerted by the change in the volume of gaps filled with lubricant, the mass flow rate of lubricant at the entrance to the system, which simulates the increase in pressure in the lubrication system of the friction unit. The results obtained do not contradict the conclusions reached in works on similar topics, and can be used in further research.
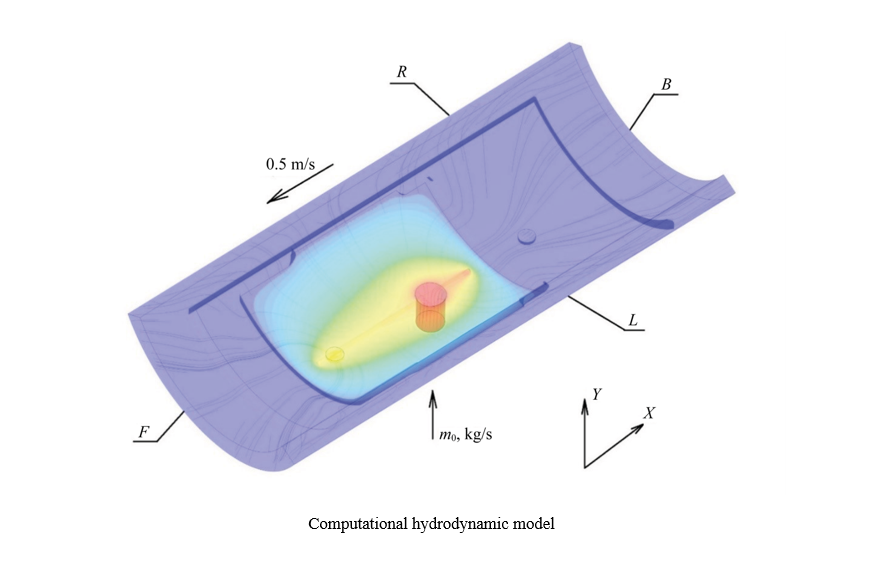
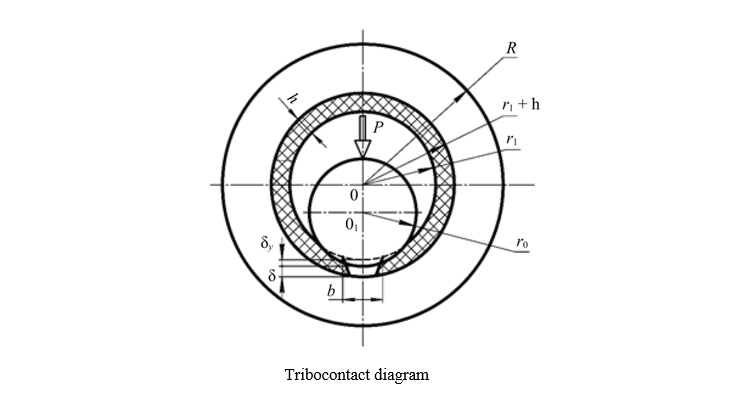
Introduction. The challenge problem of the quality of lubricants has led to both large-scale and narrow-focused theoretical and applied studies that relate to the operational properties of lubricants. In particular, the authors of the publications are interested in the interaction of bearing and lubrication, since numerous types of machinery and equipment contain these elements. In the literature, the composites used to strengthen the bearing surface are compared, the most effective compositions are determined, and the advantages and disadvantages of the components are analyzed. Mathematical models have been proposed and tested for some of the processes of the interaction under consideration, and acceptable adequacy has been proved for some of them. However, the improvement of such solutions requires taking into account the specifics of the tribosystem. This issue has been poorly worked out, and the presented article is intended to fill this gap. When evaluating the wear resistance of a radial bearing, the compressibility of a high viscosity lubricant is taken into account.
Materials and Methods. The study was based on the tribocontact scheme, which included the radius of the polymer-coated shaft, the radius of the bearing sleeve, the height of the lubrication groove, and the thickness of the lubricating layer. To create new mathematical models that took into account the compressibility of the lubricant, the authors used three equations: motion of the liquid lubricant, continuity, and state. To verify the model, the results of calculations and laboratory tests were compared. In the experiments, a bearing with a groove to preserve lubrication was used. Its rotation speed, loads and temperature conditions were changed. Friction was measured using traditional methods and modern instruments.
Results. The bearing design was modified to take into account an additional factor — the compressibility of the lubricant. The new model predicted the bearing capacity of the part by 8–10% more accurately, and the coefficient of friction — by 7–9%. Fluctuations in the coefficient of friction up to 45 MPa (equivalent to a five-fold increase in load) were detected and explained. This was due to dynamic changes in the surface contact conditions and the effects of external parameters. Optimal applications of antifriction coatings based on hybrid composite materials were determined. The possibilities of practical use of calculation models of a journal bearing were expanded. Its critically important operational characteristics were evaluated in practice.
Discussion and Conclusion. The scientific research results described in this article make it possible to establish the performance characteristics of the bearing at the design stage. The significant potential of this approach has been identified in terms of increasing the reliability and durability of the studied part, and this seems to be an important step in the development of bearing and lubricant technologies. In the future, the authors intend to study such factors as temperature conditions, dynamic loads, and interaction with various lubricants. This will allow us to improve bearing designs and expand their application areas.
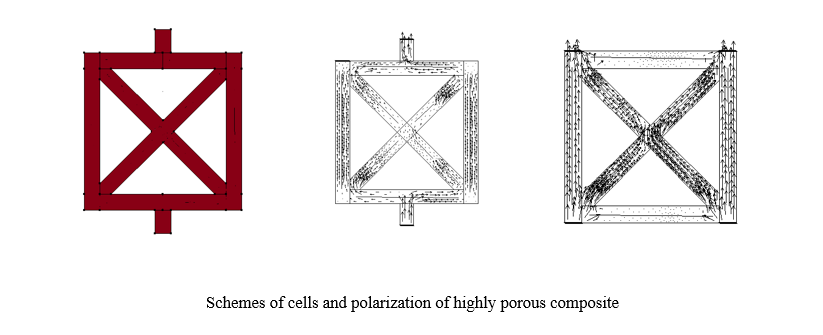
Introduction. Highly porous composites — metal foams — are widely used due to their mechanical properties. The literature presents various methods for their mathematical modeling, including those based on periodic Gibson-Ashby cells. Piezoactive composites have a number of properties, such as high sensor sensitivity and a large bandwidth. This is the reason for the interest in their modeling. However, when constructing such models from piezoceramic materials, a certain difficulty, associated with the selection of the distribution of preliminary polarization, arises. It should be noted that this issue, specifically for highly porous piezoceramics, has not been sufficiently studied in the literature. Therefore, the objective of this work was to establish the effect of the polarization model on the characteristics of the piezoactive composite.
Materials and Methods. The design material is PZT-4 piezoceramics, whose polarization depends significantly on the conditions of its guidance (model geometry, electrode arrangement). The study was divided into two steps: in the first, the residual polarization was calculated based on the theory known in the literature, the implementation of which was performed in the ACELAN package; in the second, a number of problems for a composite cell were solved, and the dependence of its properties on the polarization model was found. The finite element method implemented in the ACELAN package was used as a method for solving the corresponding boundary value problems of electroelasticity for piecewise inhomogeneous bodies.
Results. The problem of determining nonuniform polarization for two types of flat cell designs of highly porous piezoceramics was solved. Some features of the obtained polarization distribution were noted, in particular, its nonuniformity and the presence of counter polarization in some edges. The problems of determining natural frequencies and vibration modes “intra cell” and their dependence on the polarization model (homogeneous and nonhomogeneous) were solved. It was noted that some frequencies differed by 10%, while the vibration modes qualitatively coincided. The dependence of the stress-strain state and output characteristics on polarization, whose difference in some values reached 15%, was analyzed.
Discussion and Conclusion. The process of polarization of highly porous piezoceramics has a number of features that must be taken into account to obtain reliable information about its mechanical and electrical behavior. Auxetic properties, the difference in the mechanical and electrical response of the cell in question are directly related to these features. Thus, the polarization model has a significant impact on the characteristics of the piezoactive composite, which determines the importance of its correct selection. The results obtained should be taken into account when modeling representative volumes of highly porous piezoelectric composites to determine their effective properties, on the basis of which models of piezoelectric devices are constructed, and their output characteristics are calculated.
MACHINE BUILDING AND MACHINE SCIENCE
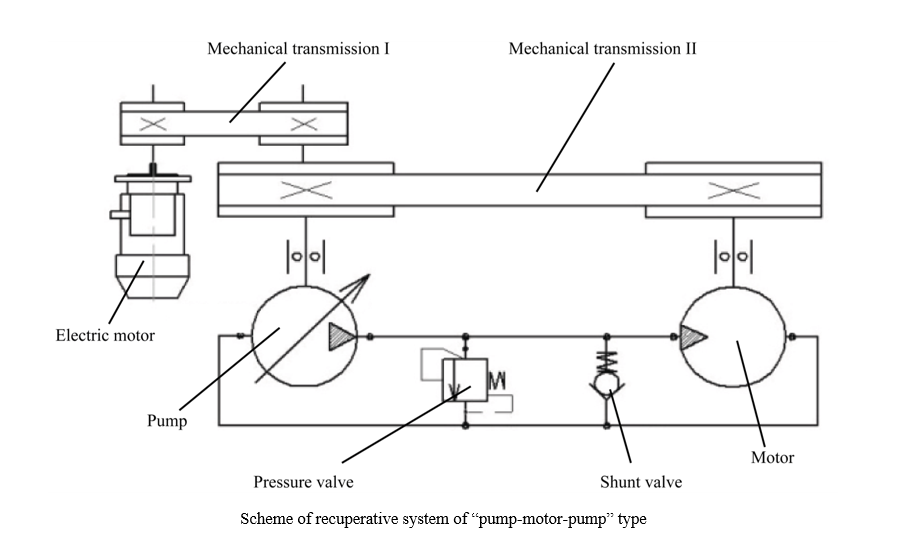
Introduction. Energy conservation is an urgent topic of research in the field of mechanical engineering all over the world. A particular direction in these studies is the search for energy-efficient methods of testing technical systems, which allow the most accurate prediction of the reliability of the designed equipment. The duration of resource tests established by technical conditions and GOSTs causes an irreversible loss of energy, amounting to more than 1.5 resource of the tested machine, and the energy lost in the form of “harmful heat” is released into the environment. Therefore, the problem of energy saving during testing is given special attention. One of the ways of energy saving under testing of hydraulic machines is energy recovery. However, in papers devoted to energy recovery during testing of hydraulic machines, the problems of energy recovery during testing of rotary hydraulic machines were solved, and for reciprocating hydraulic machines, the problem of energy recovery during testing of plunger hydraulic cylinders was solved. The results of these studies cannot be directly used for testing reciprocating hydraulic cylinders. In this regard, the objective of this work has been formulated — to develop the structure and basic scheme of a test bench for reciprocating hydraulic cylinders, providing the recovery of part of the energy spent on testing, due to which the energy efficiency of the testing process is significantly increased.
Materials and Methods. The paper used methods for modeling the process of stand functioning based on the application of the theory of volumetric rigidity. To carry out preliminary calculations of the stand operation process, a computer program based on the SimInTech software package was developed.
Results. A structural and schematic diagram of a test bench for reciprocating hydraulic cylinders has been developed. A mathematical expression has been obtained that provides a preliminary assessment of the test efficiency coefficient. A computer program based on the SimInTech software package has been created, which allows the design parameters of the stand affect its operational characteristics, including the coefficient of energy efficiency of the test process.
Discussion and Conclusion. The preliminary calculations of the operating characteristics of the stand showed that the efficiency coefficient of the proposed stand was 1.7. It can be increased by conducting additional studies aimed at obtaining rational design parameters of the stand. The proposed stand provides testing of reciprocating hydraulic cylinders with recovery of part of the expended energy, and its mathematical model allows using the numerical methods in calculations. This significantly simplifies the calculation process and increases the accuracy of the calculations. At the same time, it is possible to obtain rational parameters of the stand already at the design stage, without resorting to expensive and labor-intensive field studies.
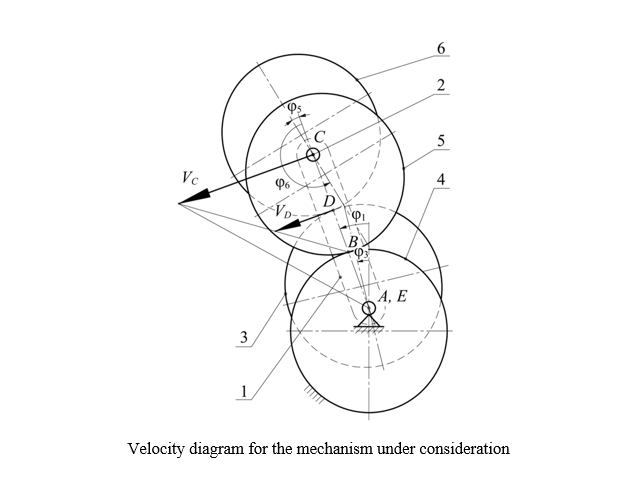
Introduction. Mechanisms with non-circular gears are of wide interest to researchers and inventors due to their compactness and the implementation of a wide range of transfer functions. The development of this area is stimulated by the advancements and reduction in cost of mechanical processing and additive manufacturing technologies, as well as the use of applied mathematical modeling packages for the analysis and synthesis of non-circular gears. Traditionally, noncircular gears are used to transmit rotational motion between parallel axes with a variable ratio of angular velocities. However, their use in planetary gear schemes provides implementing various types of output link motion. The analysis of the papers on the research area shows that gears with movable rotation axes have not been sufficiently studied from the point of view of kinematics and dynamics. Most research papers reveal the theory of such mechanisms without verifying the results obtained in practice. This work is aimed at the experimental verification of the kinematics of a planetary mechanism with two external engagements, which contains elliptical gears.
Materials and Methods. The kinematic model of the mechanism under study is built on the basis of the velocity diagram of its links, which made it possible to obtain expressions for finding an analogue of the angular velocity and the position function of the output shaft. The experimental study of kinematics was performed on a laboratory stand containing a model of a planetary mechanism with a set of replaceable gear wheels, absolute encoders on the input and output shafts of the mechanism, a controller, and a PC for recording and processing the signal. The analysis of the obtained results was performed on a computer using statistical analysis methods.
Results. As a result of kinematic analysis, position functions were constructed for three alternative planetary mechanisms, which had different geometric parameters of the gears and made it possible to implement various types of motion of the output shaft: swinging motion, discontinuous motion, and unilateral uneven rotation.
Discussion and Conclusion. The analysis of the experimental results showed the adequacy of the constructed mathematical model of kinematics to real mechanisms. The confidence interval of measuring errors at a reliability level of 95% was 0.16±0.08° for the first version of the mechanism, 0.57±0.22° — for the second version, and 0.08±0.26° — for the third. The proposed planetary mechanism with elliptical gears for implementing various types of motion can be used in drives of process equipment in numerous industries: chemical and food (mixers), oil refining (pumping units for crude production), mechanical engineering (compressors, pumps, automated machines), and others. The conducted kinematic studies of the planetary mechanism and their experimental analysis are needed for further dynamic and force investigations, as well as for the design of drives based on the proposed transmission.
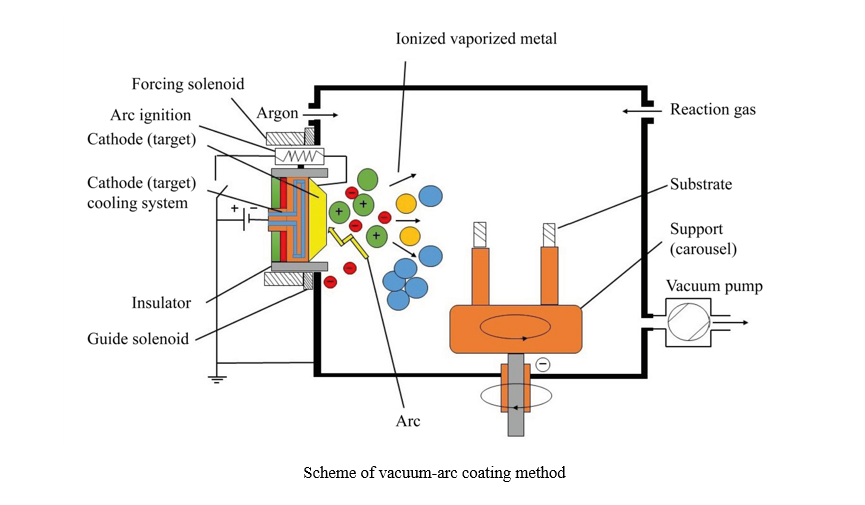
Introduction. Modern tribology solves the problems of increasing the reliability of friction units through applying vacuum wear-resistant coatings by the physical vapor deposition (PVD) method. More than five thousand scientific papers are devoted to high-entropy alloys (HEA). However, an urgent question about the possibility of obtaining wear-resistant and antifriction high-entropy coatings (HEC) using the PVD method remains unsolved. Its solution opens up the possibility of using HEC in mechanical engineering. The presented article is intended to fill this gap. Research objectives are as follows: to identify the key results on the creation of HEC by such PVD methods as vacuum arc evaporation and magnetron sputtering, to establish tribological characteristics of PVD coatings.
Materials and Methods. From November 2023 to February 2024, the authors analyzed materials published in the Web of Science, Elibrary, Scopus, Medline, CINAHL databases in the Russian and English languages.
Results. At the first stage, the literature on the vacuum arc coating method was considered. The issues of creating a vacuum arc discharge, its technological features, disadvantages, as well as processes in the cathode region of the arc were studied. The conditions of existence of cathode spots, the influence of temperature on the erosion coefficient, and processes on the anode and substrate were noted. The dependence of the deposition rate on the value of the potential on the substrate was shown. Nitride and combined coatings obtained by vacuum-arc method were analyzed: TiN, TiCN, TiAlN, TiMoS, TiSiN, TiN/VN, TiAlN/DLC-Ti. At the second stage, the history of the magnetron sputtering method was presented; technological features, types of magnetrons and nitride coatings obtained in this way were described. The third stage was devoted to the five-stage process of forming the coating structure. Island, layer-by-layer, and mixed growth modes of coating were considered. A schematic representation of the fundamental processes of structure formation was given. Defects in vacuum coatings were noted. At the fourth stage, the HEC based on the HEA were presented. Parameters predicting the formation of a HEA solid solution were indicated. Six families of high-entropy alloys were considered. Modern high-entropy coatings obtained by vacuum arc and magnetron methods were evaluated. The results of studies of structural-phase and physico-mechanical properties were summarized in the form of a table. The data of tribological studies of high-entropy coatings were presented.
Discussion and Conclusion. The literature on HEC describes the coating structure, physical and mechanical properties, and thermal stability. The authors of the presented article found a gap in the research of tribology of high-entropy coatings. From the known results, it can be concluded that these coatings are frictional. However, due to their high hardness and ductility, they exhibit high wear resistance. In addition, it is difficult to talk about their tribological purpose. To solve the issue of the possibility of using PVD coatings in mechanical engineering, attention should be paid to the development of compositions with high hardness, wear resistance, and low coefficient of friction. They can be operated in tribo-loaded nodes.
Introduction. In the public domain there is enough literature on methods of treating the musculoskeletal system. The possibilities of eliminating bone defects using patients' own (autologous) bones are described. The authors of theoretical and applied studies also suggest using synthetic bioinert materials made of polymers, calcium phosphates, plastics, and metals. The creation of three-dimensional matrices based on scaffolds for the formation of systems that are as close as possible to bone tissue in structure has been studied. It is known that the active substances of the scaffold matrix can be hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, as well as silicates, carbonates of magnesium, calcium, copper, zinc, and manganese. The issue requires detailed study. In light of the stated problem, the features of the listed materials should be considered separately. There are no such publications. The presented work is intended to fill this gap. Its objective is to create a synthesis method and study the properties of nanoscale magnesium carbonate.
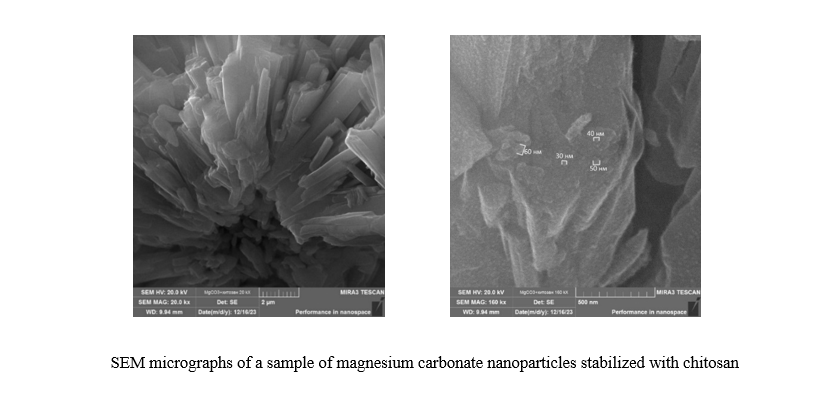
Materials and Methods. The materials for the study were samples of magnesium carbonate nanoparticles obtained by chemical precipitation in water. They were studied using X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, infrared spectroscopy, and dynamic light scattering. Quantum-chemical modeling was performed using the QChem program and the IQmol molecular editor.
Results. It has been established that magnesium carbonate particles are rod-shaped, 2 to 10 μm in length. They consist of nanoparticles from 30 to 60 nm. Quantum-chemical modeling has revealed the energy features of the interaction of the basic magnesium carbonate, firstly, with chitosan with carbonate, and secondly, with a separate chitosan molecule. In the first case, the energy value is lower, in the second, it is higher. This indicates the chemical and energetic advantage of forming such complexes. The corresponding indices for the optimal coordination of magnesium carbonate with chitosan have been determined. In this case, the interaction is provided by the hydroxyl group of chitosan attached to the C6 residue of glucosamine. For this process, the lowest energy ∆E=462.387 kcal/mol and chemical hardness η=0.062 eV are noted. Magnesium carbonate nanoparticles have optimal radius and zeta potential with the following parameters of the initial reagents: 0.018 mol of ammonium carbonate, 0.03 mol of magnesium acetate, 0.15 g of chitosan.
Discussion and Conclusion. The obtained data indicate that nanoscale basic magnesium carbonate is a promising material with a wide range of possibilities of practical application. From this point of view, its role in metabolic processes, namely in the assimilation of macronutrients, is of particular interest. Nanoscale osteotropic magnesium micronutrient synthesized in a biopolymer environment can be used as a biologically active filler for three-dimensional scaffold matrices. Implementation of this solution in medical practice will improve the efficiency of bone tissue restoration.
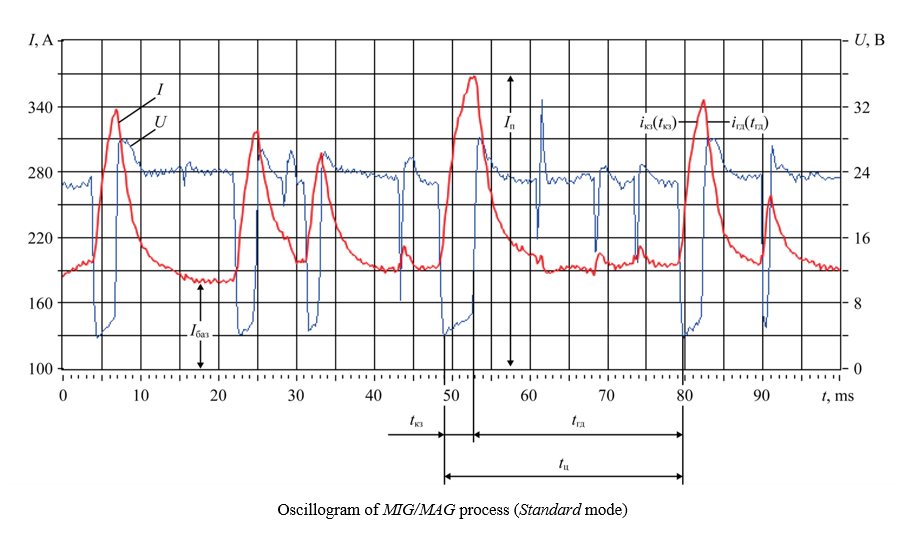
Introduction. One of the main requirements to the methods of weld overlay of sealing surfaces of power valve trim parts is to obtain a high-quality wear-resistant pad with minimal penetration and optimal process performance. Currently, arc, electroslag, plasma, beam, induction and other surfacing techniques have been developed and introduced into production. However, the influence of various arc welding processes with a consumable electrode in shielding gas on the geometric parameters of weld beads and metal hardness of sealing surfaces is understudied. The presented research is intended to fill this gap. The objective of its authors is to select such a process of arc welding of beads on parts of the power valve trim with a consumable electrode in shielding gases, which would provide the best workability of the deposited metal.
Materials and Methods. Arc surfacing with a consumable electrode in a mixture of gases was performed on steel plates. The welding torch was moved in a straight line, without transverse oscillations, using the FRC-9 mechanism (Fronius). A microprocessor-controlled inverter-type digital current source TransPulsSynergic 3200 CMT (Fronius) was used as the power supply. The following welding processes were analyzed: MIG/MAG process with self-regulation (Standard mode), synergic process of MIG/MAG method (Synergic mode), short arc process with mechanical separation of electrode metal droplets (CMT-ColdMetalTransfer), and synergic pulse-arc process (PulseSynergic). The short-cut process of bead surfacing was evaluated by the stability of the values of the energy parameters of the bead surfacing mode in time at the same electrode wire feed rates, which were recorded by oscilloscopes, as well as by comparing the geometric characteristics of the deposited beads and the hardness of the deposited metal.
Results. The analysis of experimental data of the geometrics of the weld beads and their complex dimensional characteristics made it possible to establish that the welding engineering requirements for the welded beads are most fully met by long-arc surfacing by the PulseSynergic pulse-arc process.
Discussion and Conclusion. The study and the resulting data make a certain contribution to solving the problem of the influence of arc welding processes on the parameters of weld beads and on the hardness of the metal of sealing surfaces. A detailed analysis of the modes of arc surfacing of beads with a consumable electrode in shielding gases on the trim parts of power valves can be used in further research on this topic. The conclusions of the authors will not only provide considerable theoretical assistance to scientists, but will also make adjustments to the activities of practitioners.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, COMPUTER SCIENCE AND MANAGEMENT
Introduction. In medicine and related industries, bioinspired approaches are used for the survival analysis, among which the Cox regression model holds a specific place. The practice of its application is described in the theoretical and applied literature. However, a significant drawback of this method requires careful study. The fact is that the features correlate with the hazard function linearly, and the model does not use more complex dependences. This causes some difficulties in studying survival analysis. The presented work is aimed at solving this problem. The object of study is the extended Cox model, in which the hazard function includes a nonlinear combination of features.
Materials and Methods. A database of prostate cancer patients was used, since this is a common diagnosis in global oncology. A class of extended Cox models with an additive/multiplicative hazard function was defined. To solve the problem using the optimization method, a fitness function was constructed that evaluated the results of prognosis, the number of features, and the degree of overtraining of the model — the complexity and load of the compiled hazard function. An algorithm of pollinating ants has been developed to optimize the fitness function. It simulates the reproduction of flowering plants using pollinating insects and consists of three parts: an ant colony algorithm, a genetic algorithm, and an ant pollinator algorithm. The quality of training of the Cox model was assessed by C-index.
Results. A metaheuristic algorithm for ant pollinator optimizing was proposed, providing for the construction of hazard functions of the extended Cox model. The set of parameters for training the standard Cox model was the entire set of features used: TNM, prostate-specific antigen doubling time (PSADT), Gleason score, serum PSA concentration at diagnosis, patient age and education, Rh factor. C-index value of the trained model was 0.853691. The extended Cox model with the found additive/multiplicative hazard function had a higher C-index value — 0.856241 with a smaller number of features used (TNM, PSADT, and Gleason score). In terms of quality, this approach is not inferior to or superior to the classical Cox model. Reducing the number of features involved should improve the efficiency of medical decisions and speed up the start of treatment.
Discussion and Conclusion. The presented algorithm for constructing survival analysis models increased the accuracy of predicting the occurrence of a terminal event, and reduced the number of features used for this purpose. The difference in accuracy for the studied data set seemed insignificant — C-index increased from 0.853691 to 0.856241 (by 0.3%). At this, the number of features taken into account was reduced from 7 to 3 (by 57.1%). Consequently, the proposed method effectively solves the problem of feature selection, and can be applied to improve the quality of prognostication.
Introduction. When managing traffic at the packet level in modern telecommunication networks, it is proposed to use methods that transform a self-similar stochastic packet flow into a quasi-deterministic one. To do this, it is required to apply complex probabilistic laws of distribution of self-similar flows. From the literature, methods of balancing the network load are known, which, with the problem indicated above, contribute to increasing the efficiency of telecommunication systems. However, there is no strictly mathematical solution to find out the optimal probabilistic characteristics of the output flow, based on the input flow. The presented research is intended to fill this gap. Its objective is to create a method for determining the optimal probabilistic characteristics of the packet flow, using the minimum value of the proximity measure of the self-similar input and quasi-deterministic output flows.
Materials and Methods. To solve the research problem, the parameters of the output flow distribution were selected so that the approximation function was close to 𝛿𝛿-function. The Kullback-Leibler divergence was used as a proximity measure of the input and output distributions of time intervals. Methods of set theory, metric spaces, multidimensional optimization, and teletraffic were used. The solution algorithm included minimization of the Kullback-Leibler divergence and the limit passage to 𝛿𝛿-function.
Results. A probability distribution is shown — an approximation of 𝛿𝛿-function, which maintains the equality of time intervals of a quasi-deterministic output packet flow. A method for transforming a self-similar input flow into a quasideterministic output flow is presented. The Kullback–Leibler divergence was used as a measure of their proximity. The minimum of the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the input and output flows with a normal distribution was achieved in the case of equality of the mathematical expectations of these flows. Using the passage to the limit, it has been established that time interval T between packets of the quasi-deterministic output flow must be equal to the mathematical expectation of the time intervals between packets of the input self-similar flow. To obtain a quasi-deterministic flow, the passage to the limit is performed for the found value of the mathematical expectation at σ → 0.
Discussion and Conclusion. The application of this method will reduce the negative impact of self-similarity of network traffic on the efficiency of the telecommunication network. The use of quasi-deterministic flows makes it possible to predict the load of network resources, which can be the basis for improving the quality of user service. Two difficulties associated with calculations and practical implementation of the solution are eliminated. Firstly, it is difficult to use the delta function as a function of the output flow distribution density. Secondly, there are no ideal deterministic flows in the operation of telecommunication networks. The proposed method has great potential in the design and optimization of communication networks.